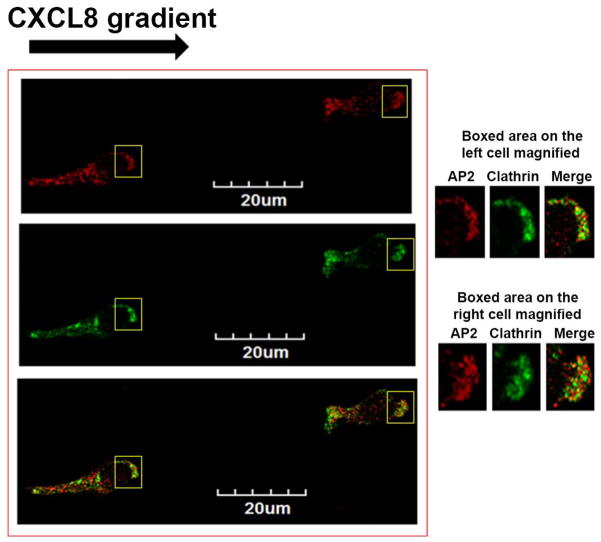
Figure 2. AP2 is essential for CXCR2-mediated chemotaxis, but β-arrestin1 is dispensable.
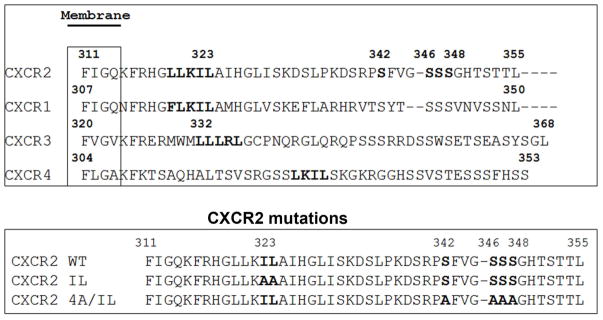
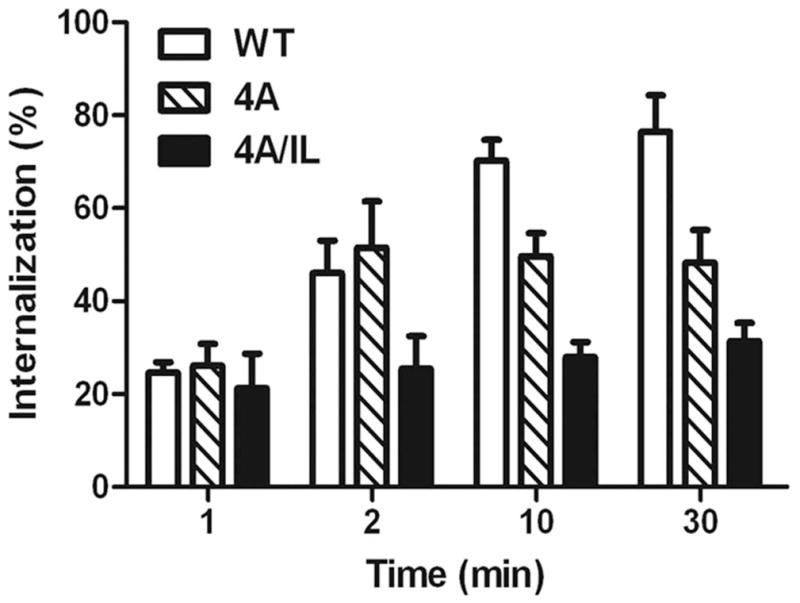
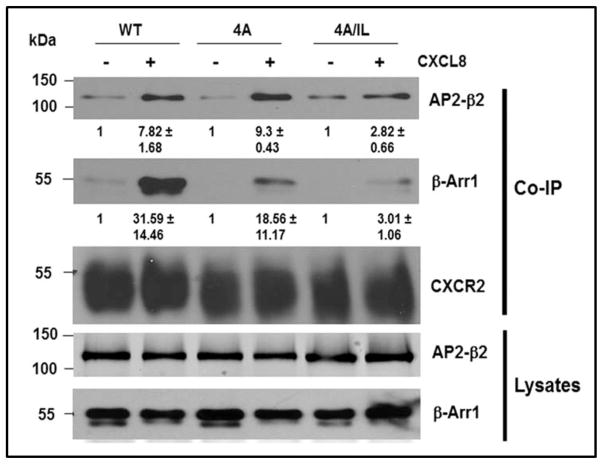
A) Top panel: LLKIL motif in CTDs of human CXC chemokine receptors is conserved. The CTDs of CXCR2 (45 residues), CXCR1 (44 residues), CXCR3 (49 residues) and CXCR4 (47 residues) were aligned with CLUSTALW (1.83) multiple sequence alignment program. The LLKIL functional motif of CXCR2 and similar putative motifs in other CXC receptor CTDs are in bold. Also, the serine residues known to be phosphorylated in CXCR2 CTD in response to CXCL8 stimulation are in bold. Bottom panel: The mutations in CXCR2 important for binding of AP2 and β-arrestin are illustrated. B) Decreased association of CXCR2 mutants with AP2 and/or β-arrestin1 after stimulation with CXCL8. dHL-60 cells stably expressing CXCR2-WT, 4A or CXCR2-4A/IL mutants were stimulated with or without CXCL8. CXCR2 was immunoprecipitated with anti-CXCR2 antibody, and blotted for AP2-β2 subunit or β-arrestin1. The blot was stripped and re-blotted for CXCR2. The relative values of fold increase in response to CXCL8 stimulation for each cell line calculated from 3 independent experiments is shown under the western blots (fold ± S.E.M.). One tenth of the total lysate input for co-immunoprecipitation was used for Western analysis of the total lysates. C) CXCL8-mediated internalization of CXCR2 is abolished in 4A/IL mutant of CXCR2, but only partially attenuated in 4A-CXCR2 mutant. The internalization of CXCR2 was performed by following the internalization of 125I-CXCL8 in dHL60-CXCR2 cells stably expressing CXCR2-WT, 4A or 4A/IL mutant. Error bars are S.E.M and the experiments were repeated 3 times with duplicates for each treatment. ANOVA: 2 min – 4A vs. 4A/IL, p<0.05; 10 min - WT vs. 4A/IL, p<0.001; 30 min – WT vs. 4A, p<0.05 and WT vs. 4A/IL, p<0.001. D) Impairment of CXCR2-mediated chemotaxis when association of AP-2 with CXCR2 is ablated by site-directed mutagenesis0. Chemotaxis assays were performed in a modified Boyden chamber with dHL-60 cells stably expressing CXCR2 WT, 4A, or 4A/IL mutants. Error bars are S.E.M and experiments were repeated 3 times with 5 replicates each treatment. ANOVA: CXCL8 12.5 ng/mL - WT vs. 4A/IL, p<0.01; 4A vs. 4A/IL, p<0.05; CXCL8 25 ng/mL - WT vs. 4A/IL, p<0.05; 4A vs. 4A/IL, p<0.01; WT vs. 4A at all of the time points – n.s.