Figure 1.
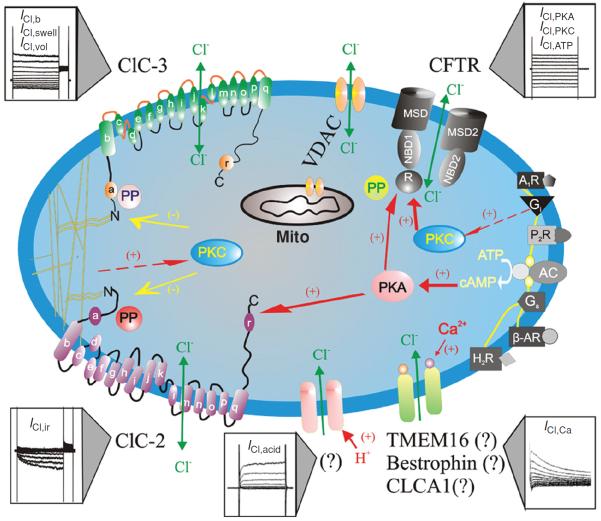
Schematic representation of Cl− channels in cardiac myocytes. Cl− channels and their corresponding molecular entities or candidates are indicated. ClC-3, a member of voltage-gated ClC Cl− channel family, encodes Cl− channels that are volume-regulated (ICl,vol) and can be activated by cell swelling (ICl,swell) induced by exposure to hypotonic extracellular solutions or possibly membrane stretch. ICl,b is a basally activated ClC-3 Cl− current. ClC-2, a member of voltage-gated ClC Cl− channel family, is responsible for a volume-regulated and hyperpolarization-activated inward rectifying Cl− current (ICl,ir). Membrane topology models (α-helices a-r) for ClC-3 and ClC-2 are modified from Dutzler et al. (61). ICl,acid is a Cl− current regulated by extracellular pH and the molecular entity for ICl,acid is currently unknown. ICl,Ca is a Cl− current activated by increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i); Molecular candidates for ICl,Ca include CLCA1, a member of a Ca2+-sensitive Cl− channel family (CLCA), bestrophin-2, a member of the Bestrophin gene family, and TMEM16, transmembrane protein 16. CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, encodes Cl− channels activated by stimulation of cAMP-protein kinase A (PKA) pathway (ICl,PKA), protein kinase C (PKC) (ICl,PKC), or extracellular ATP through purinergic receptors (ICl,ATP). CFTR is composed by two membrane spanning domains (MSD1 and MSD2), two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2), and a regulatory subunit (R). P, phosphorylation sites for PKA and PKC; PP, serine-threonine protein phosphatases; Gi, heterodimeric inhibitory G protein; A1R, adenosine type 1 receptor; AC, adenylyl cyclase; H2R, histamine type II receptor; Gs, heterodimeric stimulatory G protein; β-AR, β-adrenergic receptor; P2R, purinergic type 2 receptor; proposed intracellular signaling pathway for purinergic activation of CFTR. VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channels (porin); mito, mitochondrion (48). (Copyright Request: Duan D. J Physiol 587: 2163–2177, 2009.)