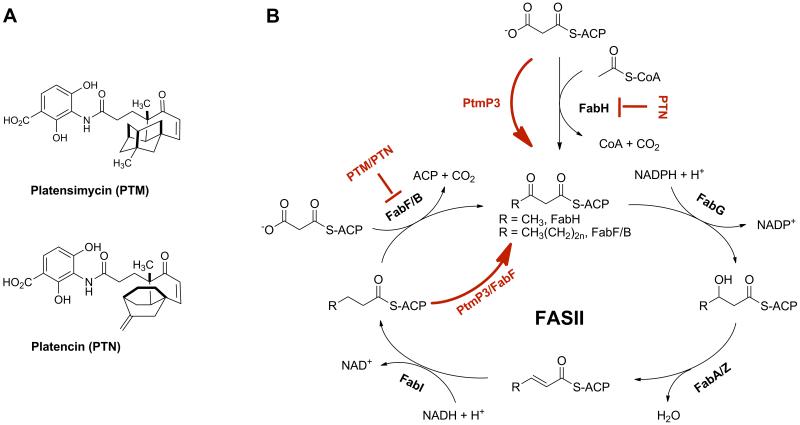
Fig. 1.
(A) Structures of platensimycin (PTM) and platencin (PTN) and (B) the bacterial fatty acid synthesis cycle (FASII). Highlighted in red are (i) PTM inhibiting FabF/B, the elongation step of FASII, and PTN dually inhibiting FabF and FabH, the initiation step FASII, and (ii) the two complementary mechanisms of PTM and PTN resistance in S. platensis by target replacement (i.e., FabF and FabH by PtmP3) and target modification (i.e., FabF by a PTM-insensitive variant). See also Figure S1.