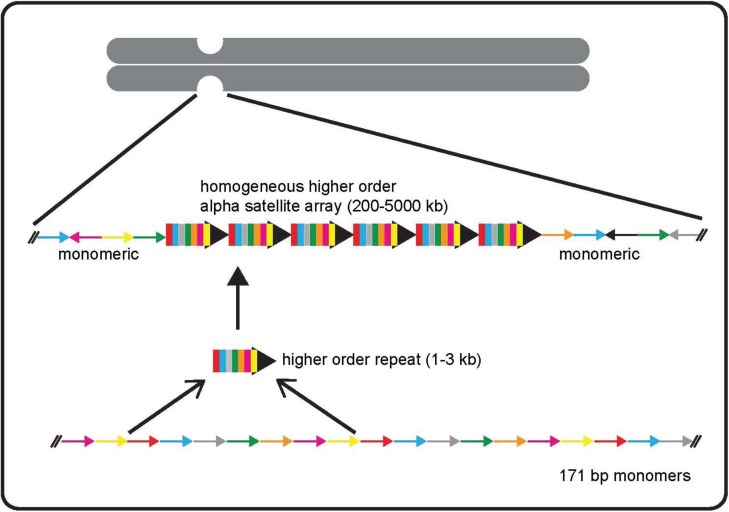
Figure 1.
The genomic organization of human centromeres. The primary sequence at human centromeres is alpha satellite DNA that is based on 171 bp monomers (colored arrows) organized in a tandem head-to tail fashion. The monomeric sequences differ by as much as 40%. A set number of monomers give rise to a higher order repeat (colored bars with black arrowhead) and confer chromosome-specificity. Higher order repeats are themselves reiterated hundreds to thousands of times, so that the alpha satellite arrays are highly homogenous and span several hundred kilobases to several megabases. Unordered monomeric alpha satellite DNA flanks the higher order arrays, becoming progressively more divergent farther away from centromeric core.