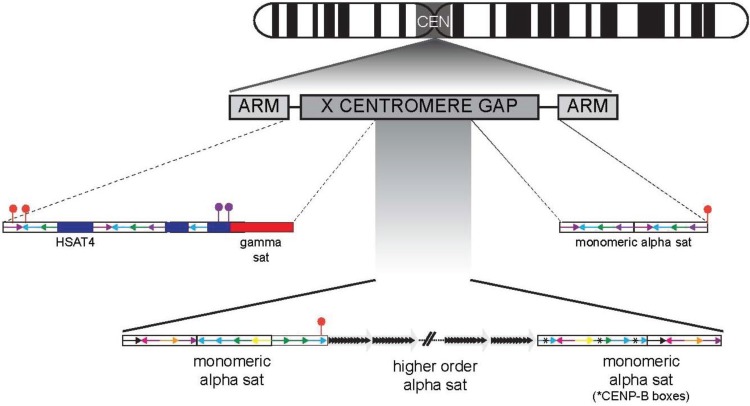
Figure 4.
The detailed genomic organization of the human X centromere. The first contiguous genomic map of a human centromere (CEN) on the X chromosome was completed in 2001 and showed that the higher order array (large light gray arrays containing black monomer arrowheads) is flanked by unordered, monomeric alpha satellite DNA (multi-colored arrows). The regions between monomeric alpha satellite and the chromosome short (Xp) and long (Xq) arms contain other types of satellite DNA, such as gamma satellite and HSAT4. LINEs (red lollipops) and SINEs (purple lollipops) punctuate the repetitive DNA between the centromere and chromosome arms. The Xq pericentromere contains monomeric alpha satellite and a LINE element at the pericentromere-arm junction. Some of the monomers within the unordered Xq satellite contain CENP-B boxes (black asterisks). The functional significance of these monomers remains unclear.