Figure 1.
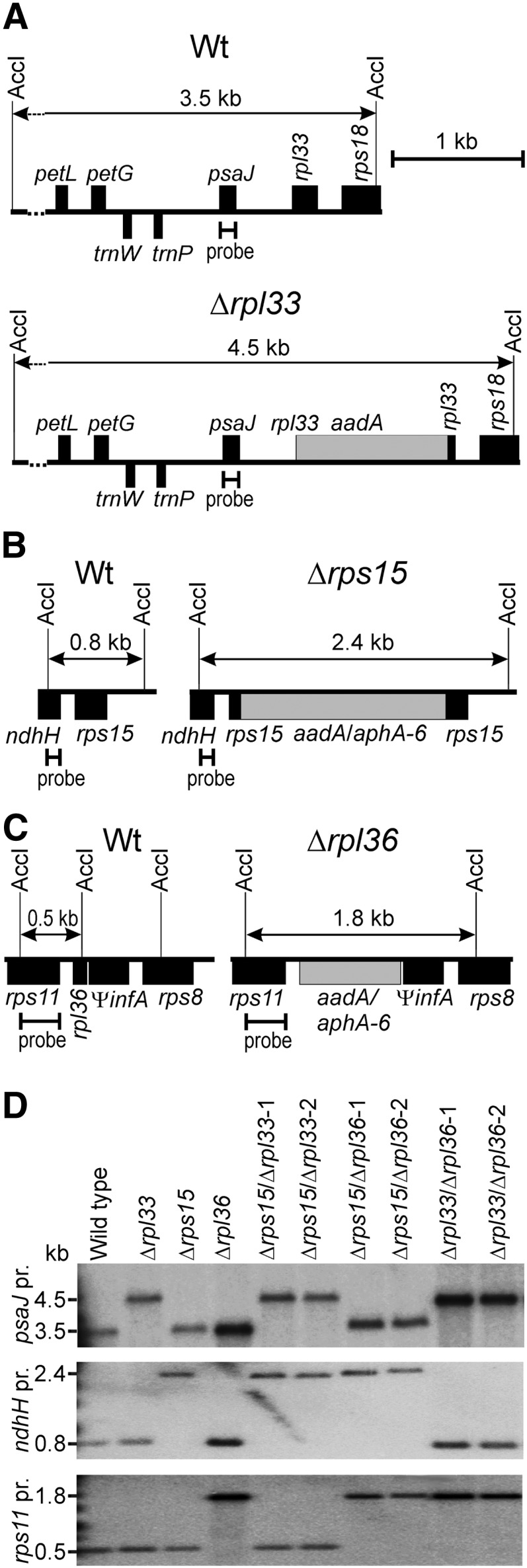
Construction of Transplastomic Double Knockout Plants for the Nonessential Ribosomal Protein Genes rps15, rpl33, and rpl36.
(A) Physical map of the region in the tobacco plastid genome (Shinozaki et al., 1986) containing the rpl33 gene and map of the transformed plastid genome (transplastome) in Δrpl33 mutant plants (Rogalski et al., 2008). Genes above the line are transcribed from the left to the right, and genes below the line are transcribed in the opposite direction. The AccI restriction sites employed for RFLP analyses are indicated, and the resulting fragment sizes are given for the wild type and the rpl33 knockout. The hybridization probe used for DNA gel blot analysis (derived from the psaJ coding region) is also indicated.
(B) Map of the genomic region containing rps15 and map of the transformed plastid genome in Δrps15 mutants (Fleischmann et al., 2011). In the Δrps15 single mutant and the Δrps15/Δrpl36 double knockout, the spectinomycin resistance marker aadA (Svab and Maliga, 1993) disrupts the rps15 gene, whereas in the Δrps15/Δrpl33 plants, rps15 is inactivated with the kanamycin resistance gene aphA-6 (Huang et al., 2002).
(C) Map of the genomic region containing rpl36 and map of the transformed plastid genome in Δrpl36 mutants (Fleischmann et al., 2011). In the Δrpl36 single mutant, the aadA marker disrupts the rpl36 gene, whereas in the Δrps15/Δrpl36 and the Δrpl33/Δrpl36 double knockout plants, rpl36 is inactivated with the aphA-6 marker.
(D) RFLP analysis of plastid transformants. The wild type, the three single mutants, and the three double knockouts (two independently generated transplastomic lines each) were analyzed by DNA gel blotting using the restriction enzyme AccI and specific radiolabeled probes (pr.) for each of the three knockout alleles (cf. panels [A] to [C]). Note that all transplastomic lines included in this blot are homoplasmic and show exclusively the bands diagnostic of the transgenic plastid genomes.
