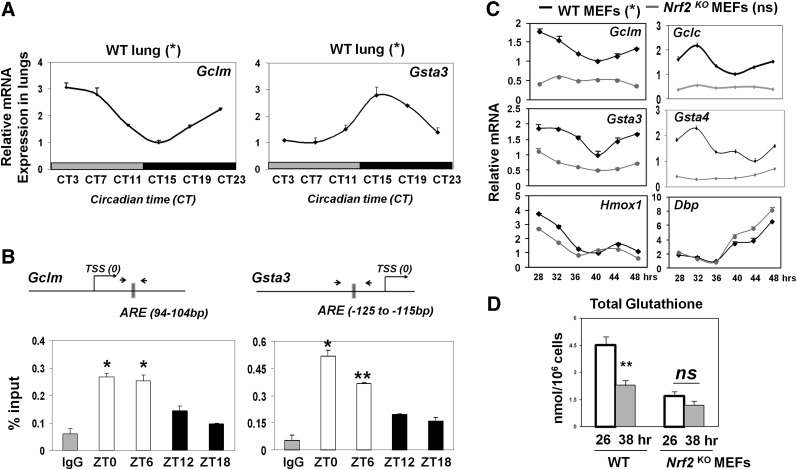
Figure 3.
Circadian rhythm of NRF2 binding to ARE drives rhythmic oscillations of genes involved in glutathione synthesis and utilization. (A) Temporal mRNA levels of NRF2 targets in wild-type (WT) mouse lungs (DD). Data (mean ± SEM) were normalized to Gapdh, and the lowest expression was set as 1. (*) P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA. (B) Rhythmic NRF2 occupancy on AREs of antioxidant gene promoters in wild-type mouse lungs by NRF2-specific ChIP. The position of each ARE in relation to the TSS is shown. Mean ± SEM. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01, t-test. (White bars) Light phase; (black bars) dark phase. (C) Temporal mRNA profiles of NRF2 target genes and clock gene Dbp in MEFs from wild-type and Nrf2 knockout (KO) mice following serum shock. Harvest of cells started at 28 h after serum shock. Data (mean ± SEM) were normalized to Gapdh. (*) P < 0.05 for all six genes in wild type; not significant for Nrf2 knockout MEFs (except Hmox1 and Dbp; [*] P < 0.05), one-way ANOVA for the effect of time. (D) Temporal levels of reduced glutathione (GSH) in MEFs from wild-type and Nrf2 knockout mice following serum shock. Data (mean ± SEM) were normalized to cellular counts and quantified using standard curve for reduced GSH. (**) P < 0.01; (ns) not significant, t-test.