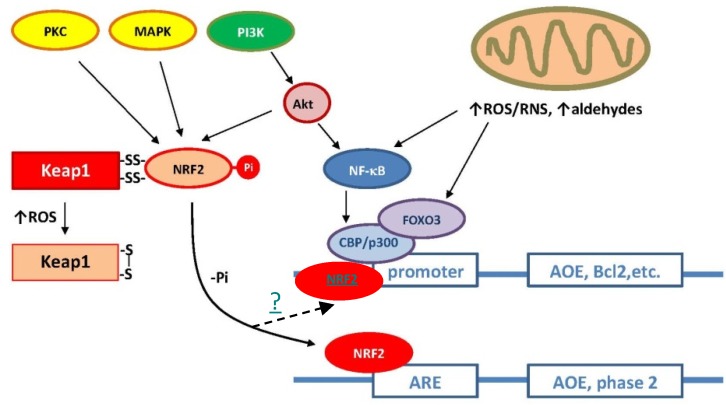
Figure 1.
Main antioxidant signaling pathways in mammals. Under normal conditions (elevated intracellular reduced potential), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is stabilized through binding to Keap-1 in the cytoplasm. Under oxidative stress, thiol groups in Keap-1 are oxidized (e.g., S-S crosslinks) causing the dissociation of Nrf2, translocation to the nucleus, and binding to the antioxidant-responsive elements (ARE). Depending upon the binding site present in the promoter region, different antioxidant genes are induced.