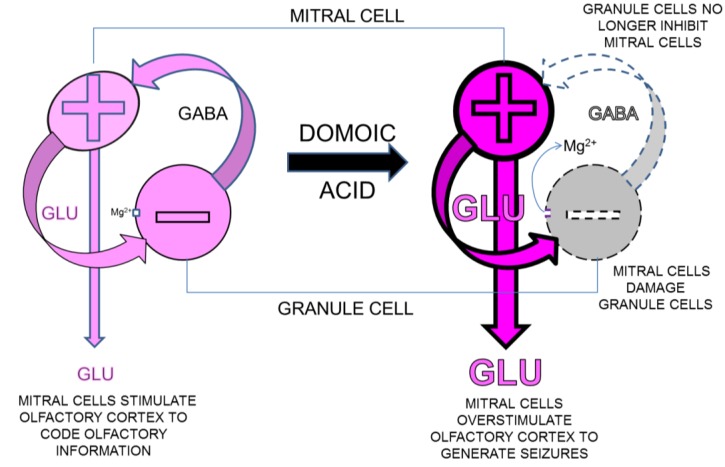
Figure 3.
Proposed mechanism for domoic acid induced damage to granule cell dendrodentric contacts with mitral cells in olfactory bulb in rat model for domoic acid epileptic disease. Left: Activation of mitral cells releases glutamate (GLU) into the dendrodentric space. The depolarization of dendritic spine of granule cells relieves magnesium block on NMDA receptor allowing glutamate induced calcium entry and release of GABA. GABA feeds back to hyperpolarize lateral dendrites of mitral cells. Right: Excitotoxic damage of dendritic spines (broken lines) disrupts GABAergic feedback at dendrodentric contacts to promote hyperactivity (bold lines) of mitral cells lack due to loss of inhibition of lateral dendrites.