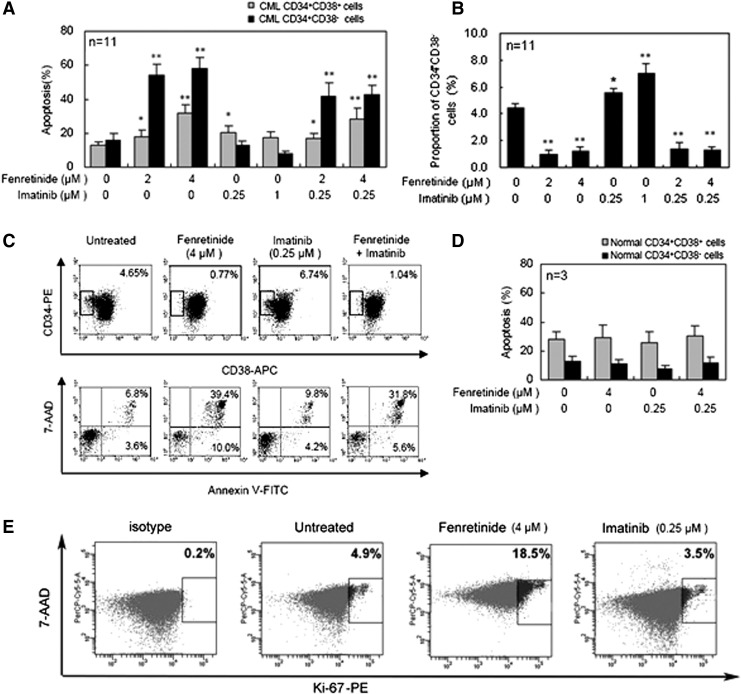
FIG. 3.
Targeting CD34+CD38− CML cells while sparing normal counterparts by fenretinide. (A) Apoptosis rate of CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ CML cells under the indicated drug exposure for 48 h in SFM. Compared with the untreated control, fenretinide alone and the co-treatment markedly induced apoptosis of CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ CML cells, especially the CD34+CD38− cells. CD34+ cells were stained with CD34-PE, CD38-APC, AnnexinV-FITC, and 7-AAD, and then tested by flow cytometry analysis. (B) The proportion of CD34+CD38− cells under the indicated drug exposure. Compared with untreated control, fenretinide alone and the co-treatment markedly decreased the proportion of CD34+CD38− CML cells. (C) Representative flow cytometry dot plots showing the effects of fenretinide and imatinib on CD34+CD38− CML cells. The bottom panels show the apoptosis rate of CD34+CD38− CML cells linked to the top panels. Numbers on the top panels indicate the proportions of CD34+CD38− CML cells after 48 h of drug exposure, and numbers on the bottom panels represent the apoptosis rates. (D) Apoptosis rate of normal CD34+CD38− and CD34+CD38+ cells induced by the indicated drug treatments. The CD34+ cells were derived from three normal donors. No significant difference was observed for each pair-wise comparison. (E) Flow cytometry dot plots showing Ki-67 expression of CD34+ cells population. Proportions of quiescent cells under the indicated drug exposure are lacking expression of Ki-67, as normalized by isotype. Compared with untreated control, fenretinide greatly increased the proportion of Ki-67+ cells. Error bar represents SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, respectively denote the statistically significant level of difference between the drug treatments and the untreated control. 7-AAD, 7-aminoactinomycin; SFM, serum-free medium.