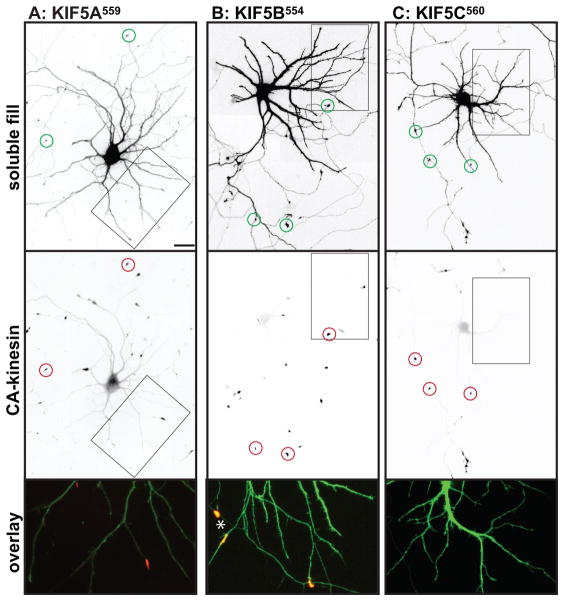
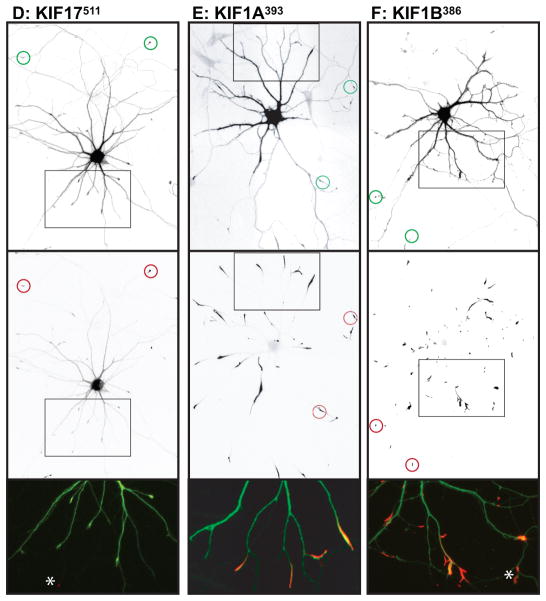
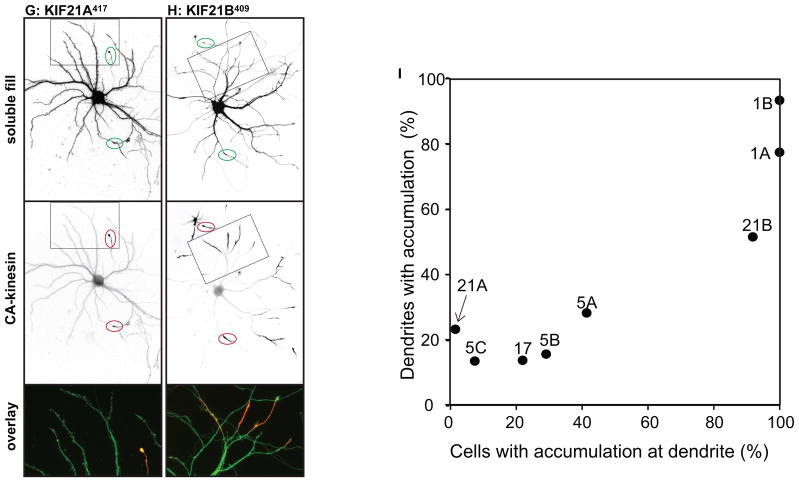
Figure 2. Different homodimeric kinesins exhibit different translocation selectivites in cultured hippocampal neurons.
(A–H) To evaluate the translocation preferences of members of the Kinesin-1, −2, −3, and −4 families, truncated kinesins tagged at their C-termini were expressed in stage 4 neurons. Several kinesins accumulated exclusively at axon tips whereas others accumulated at dendritic tips as well. The upper panels illustrate cell morphology, based on signals (γ-value adjusted) from co-expressed soluble fluorescent protein, and the middle panels show the distribution of truncated kinesins. In the lower panels, which show enlargements of the boxed regions that contain multiple dendritic tips, the kinesin is shown in red and the soluble fill in green. Axonal tips are indicated by circles in the upper panels and asterisks in the enlargements. (I) Quantification of the selectivity of each kinesin construct (based on the analysis of 29–81 cells). The X-axis indicates the percentage of transfected cells with kinesin labeling of at least one dendritic tip. For those cells with dendritic labeling, the percentage of dendritic tips that were labeled is shown on the Y-axis. Scale bars: 20μm. Images shown in panels A, B, D, and E are composites of 4 to 9 microscopic fields assembled into a single image as described in Materials and Methods.