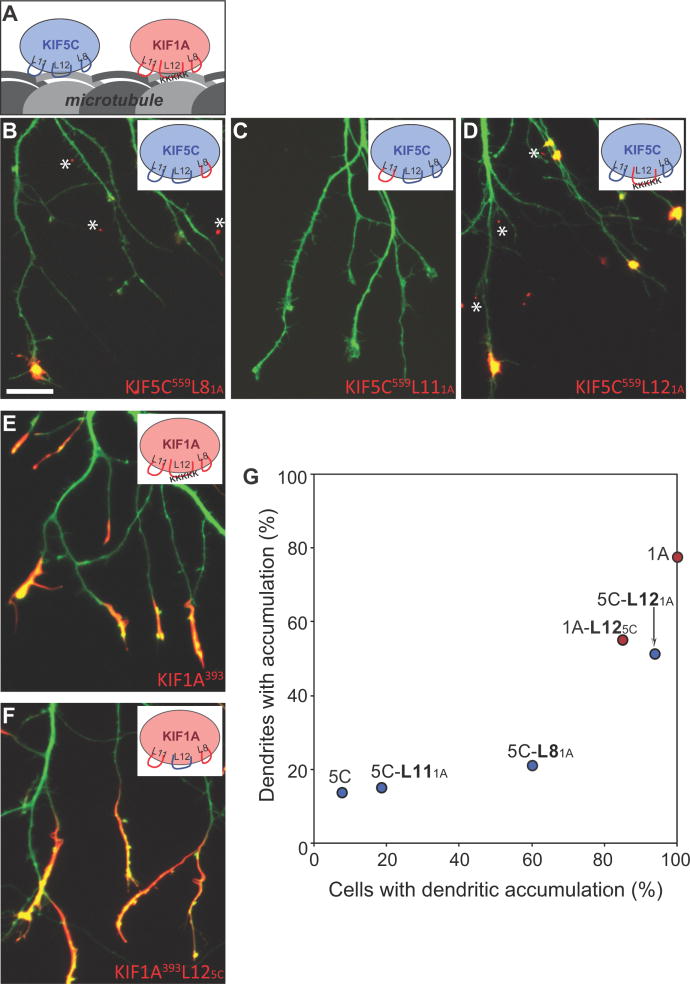
Figure 6. Two loops in the microtubule binding domain of KIF5C determine its selective translocation to axons.
(A) Cartoon illustration of the three MT-binding loops (L8, L11, and L12) of KIF5C and KIF1A. (B–D) Localization of chimeric kinesins in which each of the microtubule binding regions of KIF5C559 was exchanged with the corresponding region of KIF1A. Replacement of L12 caused KIF5C to accumulate at nearly all dendritic tips; replacement of L8 also increased dendritic labeling, but to a lesser extent. When KIF5C559 constructs translocated to dendrites, they accumulated in tiny spots (asterisks) rather than elongated segments like KIF1A. (E, F) Exchanging the L12 of KIF1A with that of KIF5C did not alter the localization of truncated KIF1A393. (G) Translocation preferences of KIF5C559 and KIF1A393 chimeric constructs, based on the analysis of 29–82 cells quantified as in Fig. 2. Data for wild type KIF1A and KIF5C were taken from the experiment shown in Figure 2I. Scale bar: 20μm.