Figure 3.
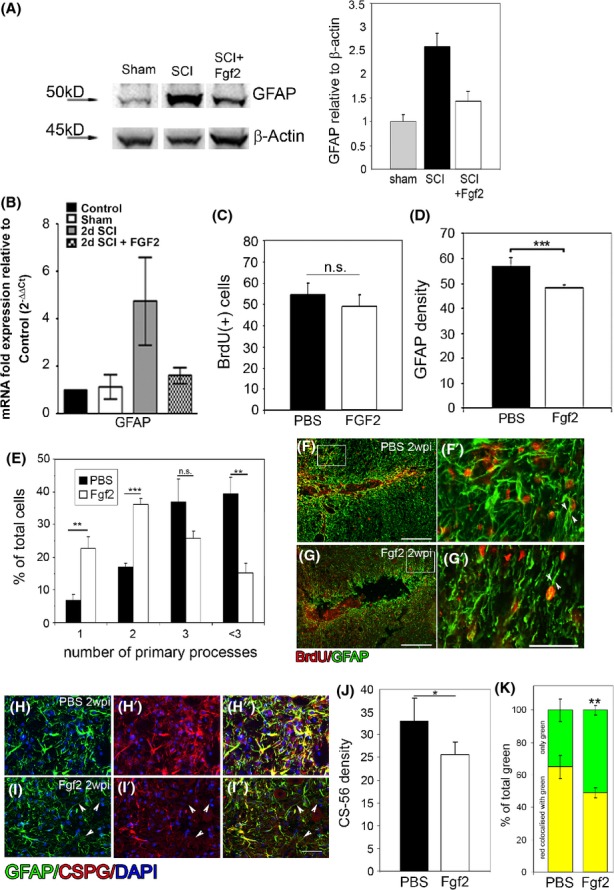
Fgf2 decreases astrocyte reactivity at the lesion site. Seven days after SCI, (A) western blot analysis shows increase in GFAP protein level after injury compared to sham operated. Fgf2 decreases GFAP protein levels after SCI (n = 3). Two days after SCI (B), Fgf2 decreased GFAP mRNA as shown by qPCR (con n = 2; sham n = 2; SCI n = 5; SCI +Fgf2 n = 4). Two weeks after SCI (C), no difference in BrdU-positive cells at the lesion site between PBS and Fgf2 treatments, although (D) GFAP density is significantly reduced after Fgf2 treatment (**P < 0.01). (E) Quantitation of the number (mean ± SEM) of primary processes extending from the cell body in control (PBS) and Fgf2 treatment (n = 6 in each group; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s. = nonsignificant) shows an increased number of cells with bipolar morphology in FGF2-treated mice. (F) Astrocytes (GFAP+ green) proliferate (BrdU+ red) in PBS-treated mice (n = 5) and exhibit thick multiprocess morphology (G′). In Fgf-treated mice (n = 5) (G), proliferating astrocytes (GFAP+/BrdU+) exhibit a bipolar morphology (G′). Immunostaining for CSPGs (J) 2 weeks after lesion revealed that their secretion was diminished in the Fgf2-treated mice (*P < 0.05) and (K, H–H′′, and I–I′′) some GFAP-positive staining dose not labeled with CSPGs (**P < 0.01 in K; I–I′′; arrowheads). Results are mean cell number in the field ±SEM. Scale bars in F and G are 200 μm, in F′, G′, H–H′′ and I–I′′ are 50 μm. Fgf, fibroblast growth factor; SCI, spinal cord injury; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; PBS, phosphate buffered saline; CSPGs, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans.
