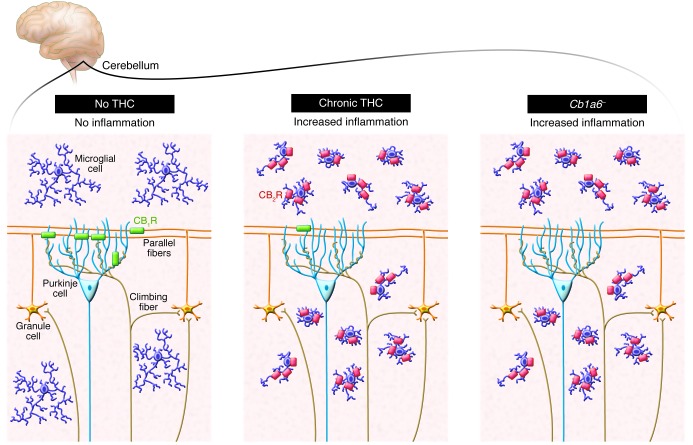
Figure 1. In mice, subchronic treatment with THC leads to the downregulation of presynaptic cannabinoid CB1 receptors expressed by parallel fibers that project onto Purkinje cells.
Cutando et al. (9) show that the loss of CB1 receptors, either due to TCH-induced downregulation or genetic deletion, triggers a neuroinflammatory response typified by changes in microglial cell morphology and CB2 receptor expression. This adaptive response underlies THC-induced deficits in cerebellar-associated learning functions.