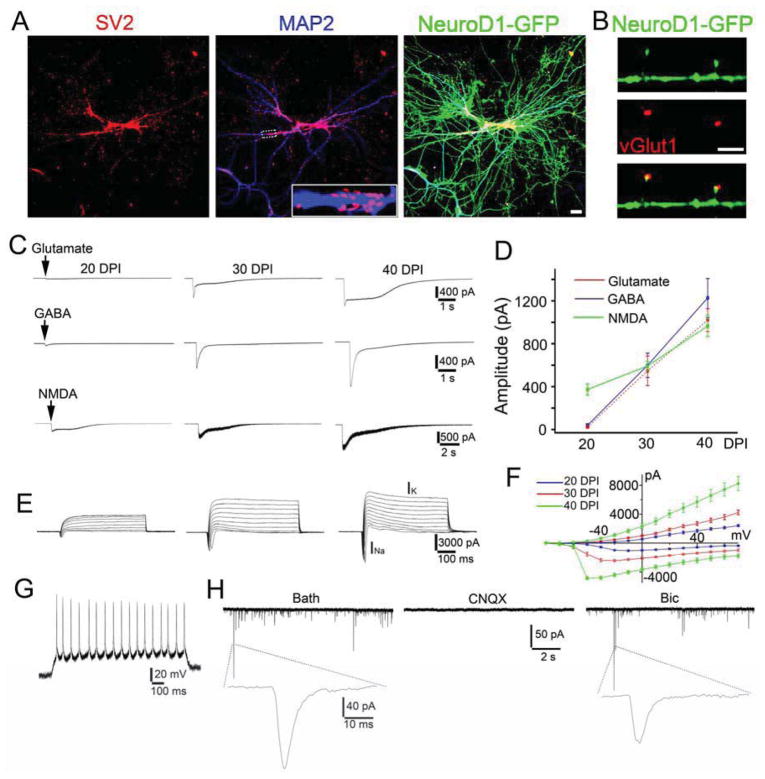
Figure 6. Functional characterization of human astrocyte-converted neurons.
(A) Synaptic puncta (SV2, red) on the dendrites (MAP2, blue) of human astrocyte-converted neurons (green, 45 DPI) after NeuroD1 infection. (B) High power image showing VGlut1 puncta (red) co-localized with dendritic spines on NeuroD1-converted neurons. Scale bars: 20 μm for panel (A); 10 μm for panel (B). (C–D) Representative traces (C) and quantitative analysis (D) of the receptor currents induced by bath application of glutamate (100 μM), GABA (100 μM), and NMDA (100 μM). (E–F) Representative traces of Na+ and K+ currents (E) and their I–V curve (F) recorded from NeuroD1-converted neurons. (G) Representative trace of repetitive action potentials in NeuroD1-converted neurons (20 DPI). (H) Representative traces of spontaneous synaptic events in NeuroD1-converted human neurons (40 DPI). Note that all synaptic events were blocked by CNQX (10 μM) but not by Bic (20 μM), suggesting that human astrocyte-converted neurons induced by NeuroD1 expression were glutamatergic neurons.