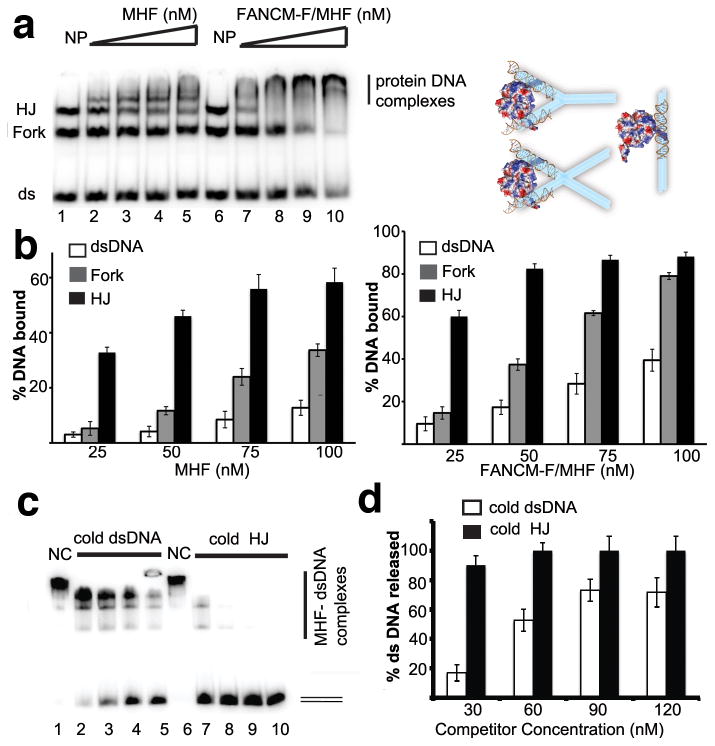
Fig. 4.
MHF binds branched DNA preferentially over dsDNA. a, Left, analysis of MHF and FANCM-F/MHF complex for binding dsDNA, forked DNA and HJ DNA. Radiolabeled DNA substrates (30 nM each) were incubated with increasing amounts of MHF (Lanes 2–5) or FANCM-F/MHF complex (Lanes 7–10) in the presence of 150 mM KCl. NP - no protein added (Lanes 1 and 6). Right, schematic depicting binding of MHF to forked DNA, HJ, or dsDNA, the charged surface is generated from MHF-DNA1. MHF tetramers are shown as electrostatic surfaces, the observed DNA duplexes are shown as brown helices, and the DNA substrates used in mobility shift assays are illustrated as cyan bars. b, Quantification of the results is shown in the bar graphs. Error bars were generated from the standard deviation in triplicate experiments. The left panel shows the data for MHF alone, while the right panel shows the data for the FANCM-F/MHF complex. c, Experiments in which a pre-formed MHF-dsDNA nucleoprotein complex was challenged with a cold DNA substrate. MHF complex (100 nM) was preincubated with radiolabeled dsDNA (30 nM). Increasing amounts of unlabeled dsDNA (Lanes 2–5) or HJ (Lanes 7–10) was added (30, 60, 90 and 120 nM). NC - control with no DNA competitor. d, Quantification of the results shown in (C). Error bars were generated from the standard deviation in triplicate experiments.