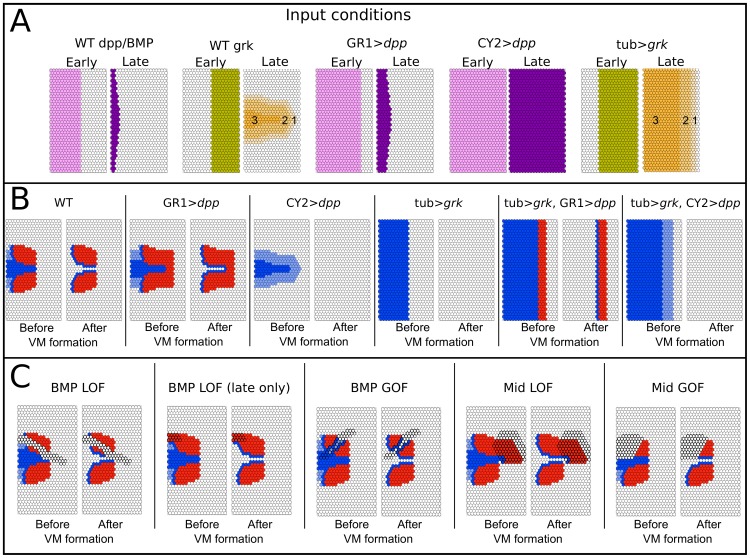
Figure 6. Perturbations of the anterior domain.
(A) Simulation of wild type inputs, and of dpp mild and strong overexpression (using GAL4 drivers GR1 and CY2) [43], [63], [75], [83], and grk overexpression (using the Tub Gal4 driver). Asymmetry is maintained in GR1 and Tub driven inputs, taking into account the cumulative effect of the Gal4 driver and wild type expression. (B) Simulation results, pre- and post-Grk extinction, obtained from combinations of the input conditions described above. The boxes show the resulting patterns of Br (roof, red) and Rho (floor, blue). Compare to Shravage et al. 2007, Figure 3, panels Ea/Ec; Fa/Fc; Ga/Gc; Ha/Hc; Ia/Ic; Ja/Jc respectively [43]. (C) Perturbations of the BMP pathway and of Mid; LOF = loss-of-function; GOF = gain-of-function. BMP LOF was simulated by setting both the early_BMP and Dpp inputs to 0, to simulate a disruption of the BMP pathway before it could repress Mid; BMP LOF (late only) was simulated by setting only the Dpp input to 0, while keeping the early_BMP unchanged, to simulate a disruption of the BMP pathway after it could repress Mid. BMP GOF was simulated by setting both early_BMP and Dpp to 1 in the highlighted region. Mid LOF and GOF were simulated by setting Mid to 0 or 1, respectively, in the highlighted cells.