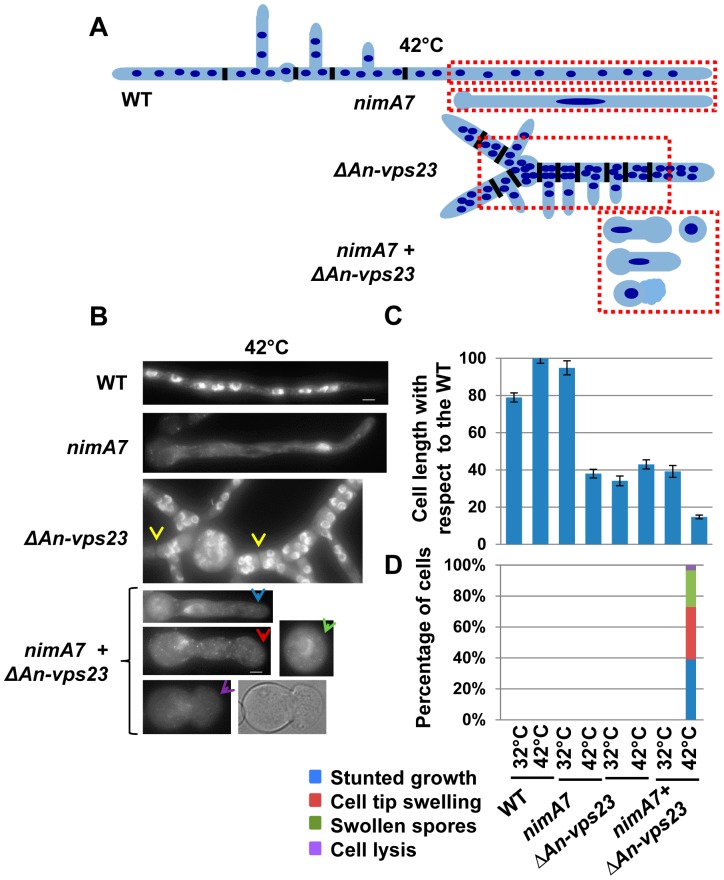
Figure 2. Deletion of An-vps23 modifies the terminal phenotype of cells lacking NIMA function.
(A) A schematic representation of the cell morphological phenotypes of WT, nimA7, ΔAn-vps23 and nimA7 + ΔAn-vps23 strains. The red dotted rectangles mark the region of the cell in each strain that is depicted in (B). (B) Representative images of the indicated strains. Closely spaced septa (as identified by bright field imaging) in ΔAn-vps23 cells are marked by yellow arrows. (C) The double mutants show a higher, statistically significant growth defect at 42°C, the restrictive temperature for the nimA7 allele (blue arrow in B) compared to either single mutant (p<0.001). (D) The double mutants display novel phenotypes not seen in either single mutant at 42°C, such as defects in germtube emergence (green arrowhead), cell tip swelling (red arrowhead), and cell lysis (purple arrowhead). Bar, 5 μm. WT = R153, nimA7 = MG44, ΔAn-vps23 = MGH21, nimA7 + ΔAn-vps23 = MGH19.