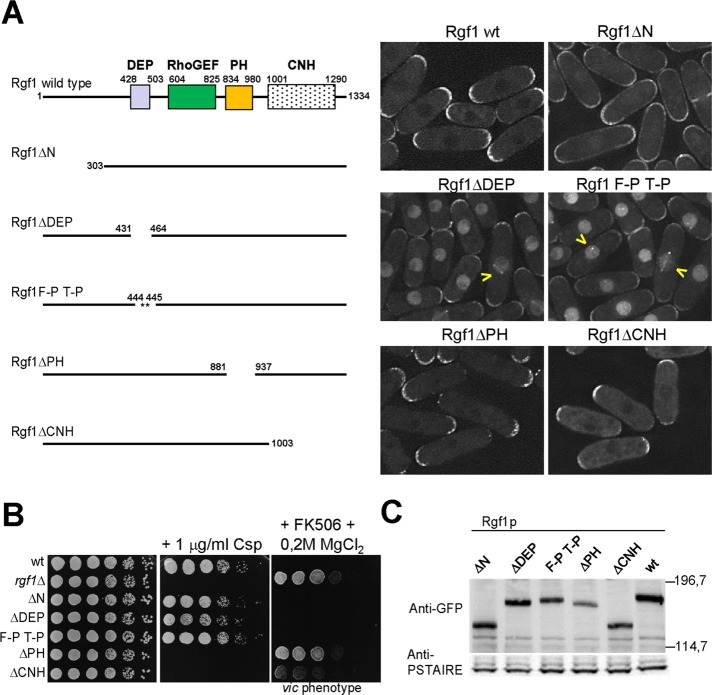
FIGURE 1:
Deletion of the Rgf1p DEP domain directs the protein to the nucleus. (A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of the full-length Rgf1p (aa 1–1334) and the various deletion fragments and site-specific mutation generated. All constructs were expressed as proteins C-terminally tagged with GFP and integrated at the leu1 locus in an rgf1Δ background. The intracellular localization of the wild-type Rgf1-GFPp, Rgf1pΔN-GFP, Rgf1pΔDEP-GFP, Rgf1pFPTP-GFP, Rgf1pΔPH-GFP, and Rgf1pΔCNH-GFP was analyzed in cells grown to early log phase in YES medium. (B) The PH and CNH domains are essential for Rgf1p function in vivo. Caspofungin (Csp) hypersensitivity and the vic phenotype of the wild-type, rgf1Δ, Rgf1pΔN-GFP, Rgf1pΔDEP-GFP, Rgf1pFPTP-GFP, Rgf1pΔPH-GFP, and Rgf1pΔCNH-GFP strains were analyzed in plate assays. Cells were spotted onto YES plates without 1 μg/ml Csp (Cancidas) as serial dilutions (8 × 104 cells in the left row and then 4 × 104, 2 × 104, 2 × 103, 2 × 102, and 2 × 101 in each subsequent spot) and incubated at 28ºC for 3 d. For the vic phenotype, cells were spotted onto YES or YES plus 0.5 μg/ml FK506 and 0.2 M MgCl2 and incubated at 32ºC for 3 d. (C) Western blot analysis showing the level of the indicated GFP-tagged Rgf1p mutants. Anti-PSTAIR antibody against Cdc2p was used as a loading control. Molecular mass markers are shown on the right of the gel in kilodaltons.