Figure 3.
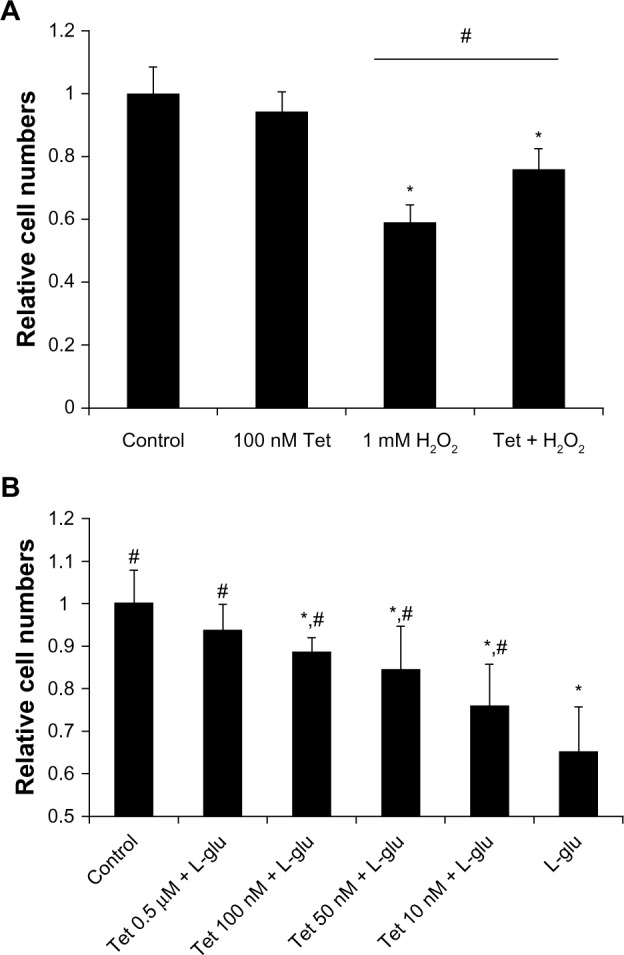
Tet protected RGC-5 cells from H2O2 injury and L-glutamate excitotoxicity.
Notes: (A) Cell death induced by H2O2 could be attenuated by the addition of Tet at a concentration of 100 nM, 6 hours prior to H2O2 exposure, as compared with RGC-5 cells treated with Tet 48 hours after exposure to 1 mM H2O2, but never reached the control level. (B) Tet pretreatments (6 hours prior to L-glutamate exposure) of 10 nM and greater were able to promote RGC-5 cell survival 12 hours after exposure to 25 mM L-glutamate, and the relative cell numbers increased as the Tet concentration increased. Tet (10 nM −0.5 μM) could increase the relative cell numbers significantly. The relative cell numbers of the 0.5 μM Tet plus L-glutamate group reached the control level, while numbers in the other Tet treated groups were lower than in the control. Results are expressed as the means ± SD. *P<0.05 compared to control; #P<0.05 compared to 1 mM H2O2 or 25 mM L-glutamate, one-way ANOVA (n≥6).
Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; L-glu, L-glutamate; SD, standard deviation; Tet, tetrandrine.
