Figure 1. DPP6a and DPP10a N-termini possess a highly conserved cysteine (Cys-13), like other N-type inactivation domains sensitive to redox regulation.
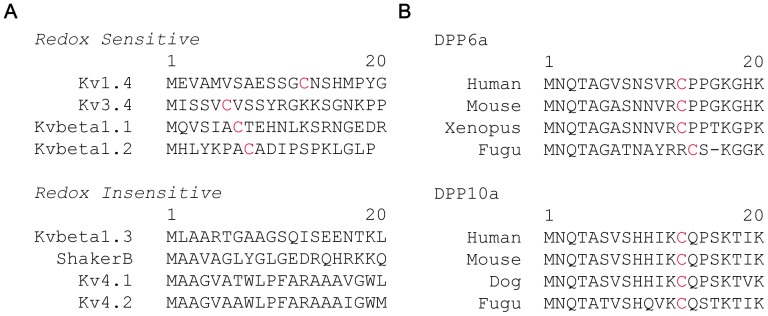
A. Alignments of the first 20 residues from the N-termini of pore-forming and auxiliary subunits known to mediate N-type inactivation. Sequences were separated into two groups based on reported redox sensitivity (see Results for reference information). B. Alignments of DPP6a and DPP10a variable N-terminal sequences (20 residues) from various species from human to fish. The unique N-terminal cysteine is highlighted in red.
