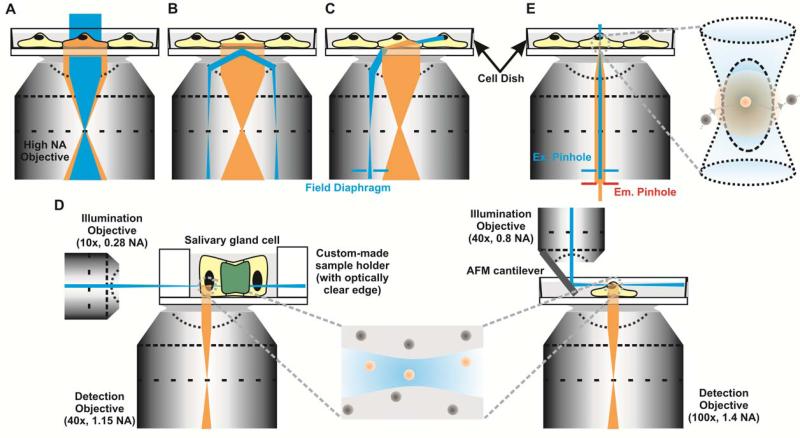
Figure 8. Various types of illumination geometries.
(A) Wide-field, (B) TIRF, (C) HILO/VAEM with a field diaphragm to reduce illumination light diameter, (D) SPI with LSFM (left) and RLSM (right) with a magnified view of the illumination plane. Although the geometry is similar for the two approaches, the dimensions of the illumination plane are very different. (E) Standard narrow-field illumination, with a blow-up of the illumination spot. Pinholes for the excitation (Ex.) light and emitted (Em.) light are used to reduce excitation volume and decrease background from out-of-focus fluorescence, respectively.