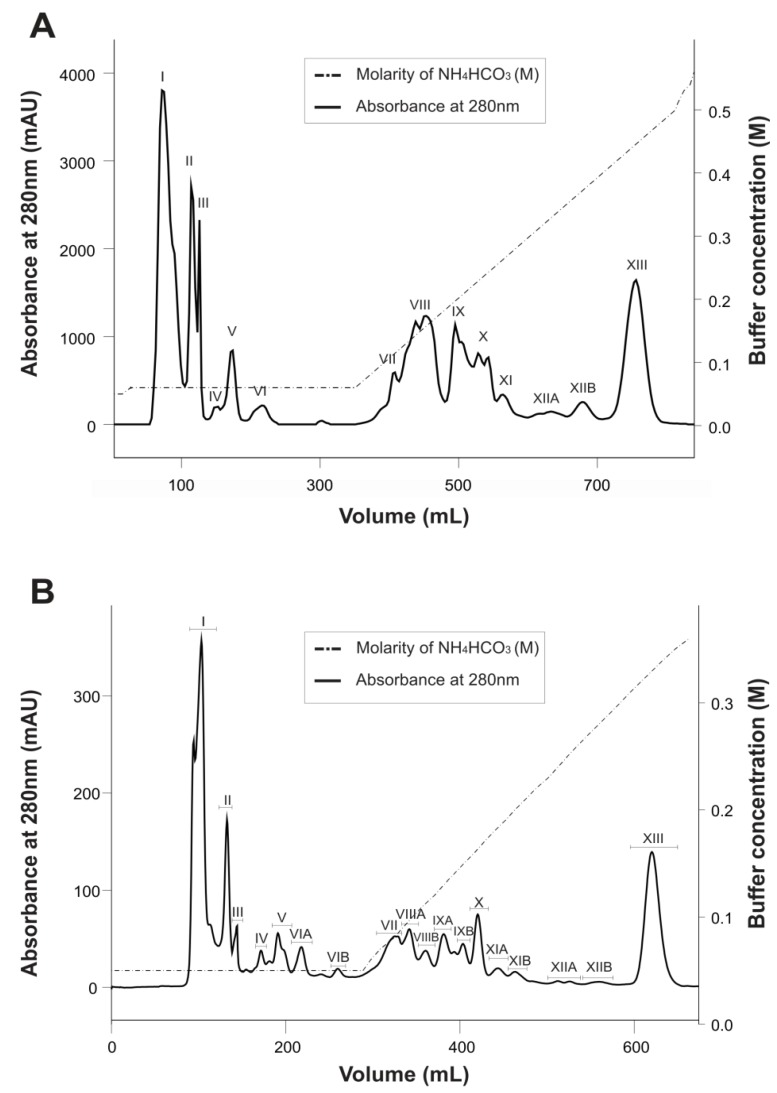
Figure 1.
Elution profile of Ts venom on CM-cellulose-52 column. Absorbance was monitored at 280 nm. (A) Classical method of fractionation. Tityus serrulatus venom (200 mg) was dispersed in 2 mL of 0.05 M NH4HCO3 and the supernatant was fractionated on a column 2.5 cm × 63.0 cm, equilibrated with 0.05 M ammonium bicarbonate, pH 7.8 (Buffer A), at 4 °C. Flow: 0.3 mL/min. The dotted line represents the beginning of the convex concentration gradient of 0.01–1 M of ammonium bicarbonate (Buffer B). (B) Improved method of fractionation using a FPLC Äkta Purifier UPC-10 system. Tityus serrulatus venom (50 mg) was dispersed in 2 mL of 0.05 M NH4HCO3 and the supernatant was fractionated on a column 1.6 cm × 100.0 cm, equilibrated with 0.05 M ammonium bicarbonate, pH 7.8 (Buffer A), at 25 °C. Flow: 0.5 mL/min. The dotted line represents the beginning of the linear concentration gradient from 0% to 100% of 0.6 M of ammonium bicarbonate (Buffer B). Absorbance was monitored at 280 nm.