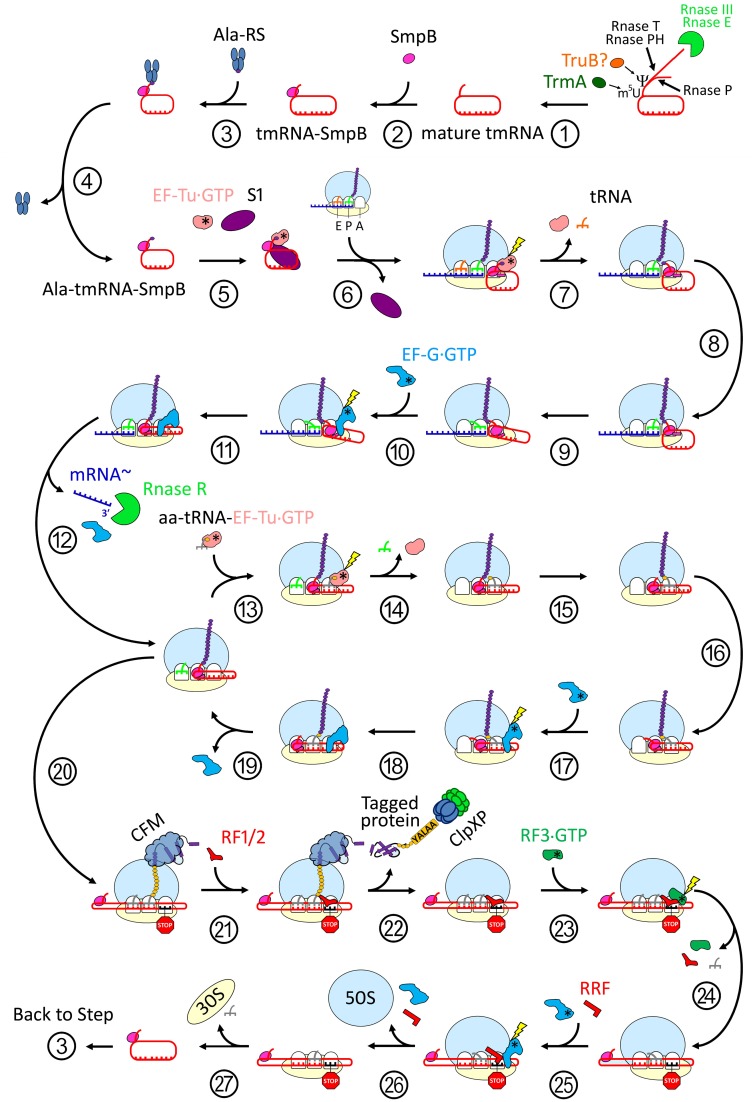
Figure 1.
The cycle of trans-translation. Maturation: (1) The tmRNA primary transcript 5′-terminus is processed by the endonuclease RNAse P, while the 3′-terminus is first cleaved by endonucleases RNAses III or E then trimmed by exonucleases RNAses T and/or PH. Nucleotides in the T-loop are modified at least twice: a 5-methyluridine is catalysed by TrmA, and a pseudouridine may be catalyzed by TruB. (2) The tmRNA-SmpB complex is formed. (3) Ala-RS charges the deacyl tmRNA-SmpB with a new alanine. (4) Ala-RS is released. (5) EF-Tu•GDP and S1 bind to Ala-tmRNAAla-SmpB, and the complex is ready to rescue a stalled ribosome. Re-registration: (6) Pre-accommodation. The ala-tmRNAAla-SmpB-EF-Tu•GTP quaternary complex binds to a stalled ribosome. SmpB recognizes the vacant A-site. S1 is released. (7) SmpB simulates the codon-anticodon recognition and induces GTPase activity on EF-Tu. Ala-tmRNAAla-SmpB accommodates into the A-Site. EF-Tu•GDP and E-Site deacyl tRNA are released. (8) Peptidyl transfer. The nascent peptide is transferred from the P-Site tRNA to the Ala-tmRNAAla. The nascent peptide is elongated by one Ala. (9) Ratchet. The 30S subunit spontaneously rotates in an anticlockwise direction relative to the 50S. This ratchet-like motion brings TLD-SmpB and tRNA into hybrid states of binding (A/P and P/E respectively). (10) EF-G•GTP binds to the ribosome, stabilizing the ratchet formation and inducing a unique 12° head tilt. (11) GTP hydrolysis. TLD-SmpB and tRNA are translocated to the P- and E-sites, respectively. The tmRNA internal ORF is positioned in the A-site. (12) EF-G•GDP and non-stop mRNA release. Subsequent degradation of non-stop mRNA by RNAse R. Elongation: translation restart on the tmRNA internal ORF: (13) aa-tRNAaa-EF-Tu•GDP ternary complex binds to the ribosome. (14) The recognition of tmRNA internal ORF codon by the aminoacyl tRNA induces GTP hydrolysis. The aa-tRNAaa is accommodated in the A-site. EF-Tu•GDP and the E-Site deacyl tRNA are released. (15) Peptidyl transfer. The nascent peptide is transferred to the incoming aa-tmRNAaa and is elongated by one amino-acid. (16) Ratchet. (17) EF-G•GTP binding. (18) GTP hydrolysis and translocation. (19) EF-G•GDP release. The process is repeated until the tmRNA STOP codon is reached. After the first cycle, like deacyl tRNAs, the TLD and SmpB are released from the E-site. Termination-recycling: (20) The tmRNA STOP codon is reached. (21) RF1 or RF2 recognize the STOP codon and bind to the A-site. (22) The class I release factor triggers P-site tRNA deacylation. The new peptide (if unfolded) or protein (if already folded by the CFM) carrying the tmRNA tag is released. A protease such as ClpXP recognizes the tag and degrades the potentially-hazardous product. (23) Class II release factor binds to the ribosome. (24) GTP hydrolysis induces a ratchet-like movement and rapid dissociation of class I and II release factors and E-site deacyl-tRNA. (25) RRF and EF-G•GTP binding. (26) GTP hydrolysis. RRF acts as a wedge, inducing dissociation and recycling of the large ribosomal subunit. RRF and EF-G•GDP are also released. (27) Deacyl tmRNA-SmpB and tRNA dissociate from the small ribosomal subunit. The 30S can be used for a new round of translation. tmRNA-SmpB is recycle. Abbreviations: Rnase III, endoribonuclease III; Rnase E, endoribonuclease E; Rnase T, exoribonuclease T; Rnase PH, exoribonuclease PH; Rnase P, endoribonuclease P; Y: pseudouridine; m5U, 5-methyluridine; TruB, tRNA pseudouridine synthase II; TrmA, S-adenosyl methionine-dependent rna methyltransferase; tmRNA, transfer-messenger RNA; SmpB, small protein B; tmRNA-SmpB, deacyl transfer-messenger RNA and small protein B binary complex; AlaRS, alanyl-tRNA synthetase; ala-tmRNA-SmpB, alanyl transfer-messenger RNA and small protein B binary complex; EF-Tu, elongation factor thermo unstable; GTP, guanosine-5′-triphosphate; S1, small ribosomal subunit protein 1; t-RNA deacyl transfer RNA; EF-G, elongation factor G; mRNA, non-stop mRNA; Rnase R, exoribonuclease R; aa-tRNA, amino-acyl transfer RNA; CFM, co-translational folding machinery; RF1/2, release factor 1 or 2; ClpXP, a protease complex; RF3, release factor 3; RRF, ribosome recycling factor; 50S, large ribosomal subunit; 30S, small ribosomal subunit.