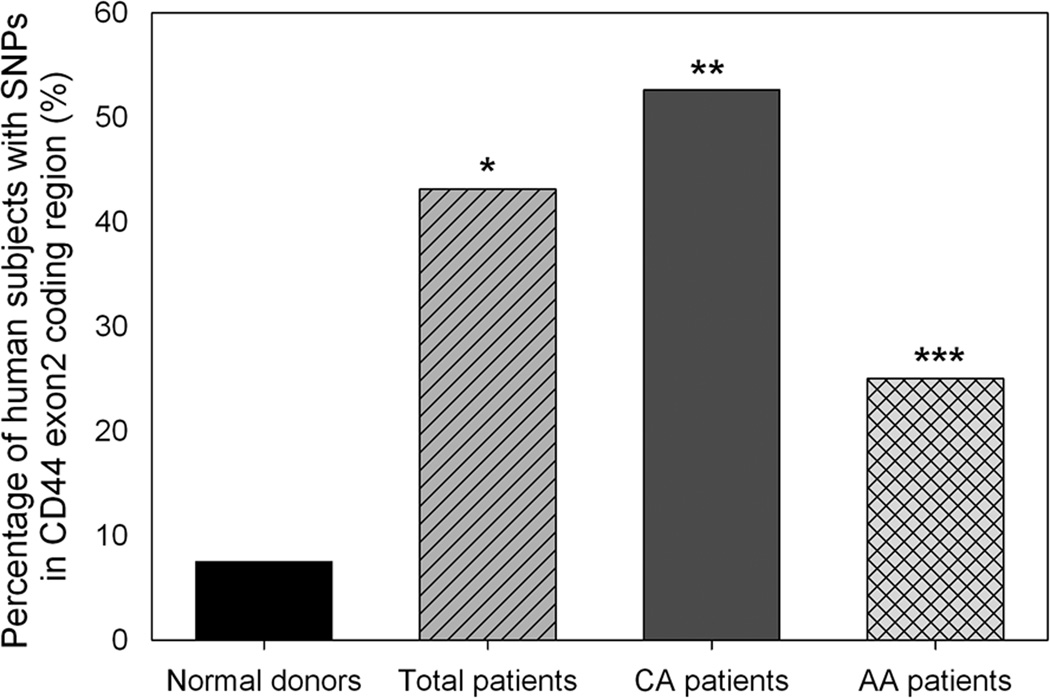
Figure 3.
Statistical comparison of CD44 polymorphisms in CD44 exon2 coding region between female breast cancer patients and normal donors. When compared to female normal donors, * indicated that the percentage of female breast cancer patients having CD44 polymorphisms in CD44 exon2 coding region was significantly higher (odds ratio = 9.34; 95% confidence interval = 2.58–33.82; p < 0.0001), ** indicated that the percentage of Caucasian American female breast cancer patients having CD44 polymorphisms was significantly higher (odds ratio = 13.70; 95% confidence interval = 3.60–52.22; p < 0.0001), and *** indicated that the percentage of African American female breast cancer patients with CD44 polymorphisms was also significantly higher (odds ratio = 4.11; 95% confidence interval = 0.87–19.41; p < 0.05). CA, Caucasian American. AA, African American. Fisher Exact test was used to determine the statistical difference of SNP frequencies between two groups.