Figure 2.
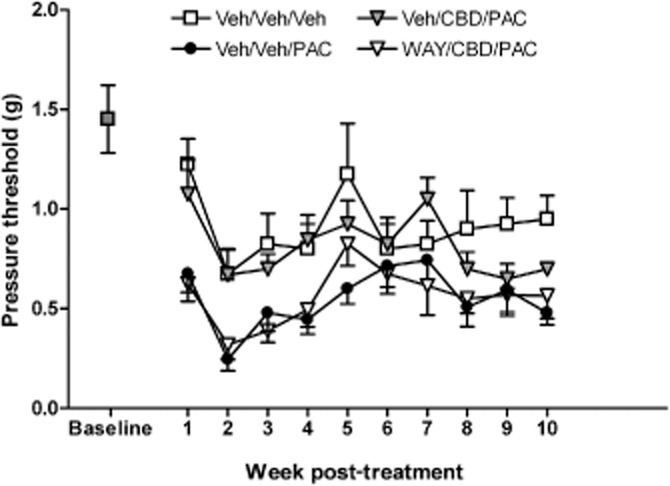
Effect of WAY100635 pretreatment (1.0 mg·kg−1, i.p.) on CBD prevention of PAC-induced mechanical allodynia in female C57Bl/6 mice. Baseline sensitivity to von Frey filaments was assessed on the day before drug administration and continued weekly for 10 weeks. Mice received the following three i.p. injections spaced 15 min apart on days 1, 3, 5 and 7: saline, CRM vehicle, CRM vehicle; saline, CRM vehicle, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; saline, 5.0 mg·kg−1 CBD, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; 1.0 mg·kg−1 WAY100635, 5.0 mg·kg−1 CBD, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC. Two-way anova revealed significant effects of treatment [F(3, 280) = 24.66, P < 0.0001] and time [F(9, 280) = 5.058, P < 0.001] and no significant interaction (F <1.0). Bonferroni post-test revealed a significant increase in the sensitivity of the PAC group and the WAY/CBD/PAC groups compared with Veh/Veh/Veh. In contrast, the Veh/CBD/PAC group did not differ significantly from the Veh/Veh/Veh group on mechanical sensitivity. X-axis: time points pre- or post-day first injection. Y-axis: threshold pressure to elicit hind paw withdrawal from von Frey filament. Data points represent the mean and SEM, n = 8 per group.
