Figure 3.
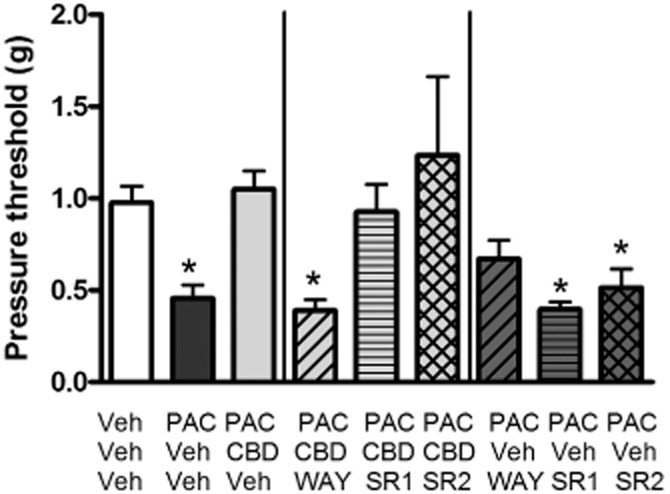
Effect of CB1 (SR141716; SR1) or CB2 (SR144528; SR2) receptor antagonism on CBD prevention of PAC-induced mechanical allodynia in female C57Bl/6 mice. Sensitivity to von Frey filaments was assessed on day 15 post-treatment. Mice received the following three i.p. injections spaced 15 min apart on days 1, 3, 5 and 7: saline, CRM vehicle, CRM vehicle; saline, CRM vehicle, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; saline, 5.0 mg·kg−1 CBD, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; 1.0 mg·kg−1 WAY, 5.0 mg·kg−1 CBD, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; 3.0 mg·kg−1 SR141716, 5.0 mg·kg−1 CBD, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; 3.0 mg·kg−1 SR144528, 5.0 mg·kg−1 CBD, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; 1.0 mg·kg−1 WAY, CRM, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; 3.0 mg·kg−1 SR141716, CRM, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC; 3.0 mg·kg−1 SR144528, CRM, 8.0 mg·kg−1 PAC. One-way anova revealed a significant effect of treatment [F(8, 79) = 7.647, P < 0.05]. Dunnett's multiple comparison test determined that only the Veh/Veh/PAC, WAY/CBD/PAC, SR1/Veh/PAC and SR2/Veh/PAC groups were statistically different from the Veh/Veh/Veh control group (P < 0.05). X-axis: treatment. Y-axis: threshold pressure to elicit hind paw withdrawal from von Frey filament. Data points represent the mean and SEM, n = 8 per group.
