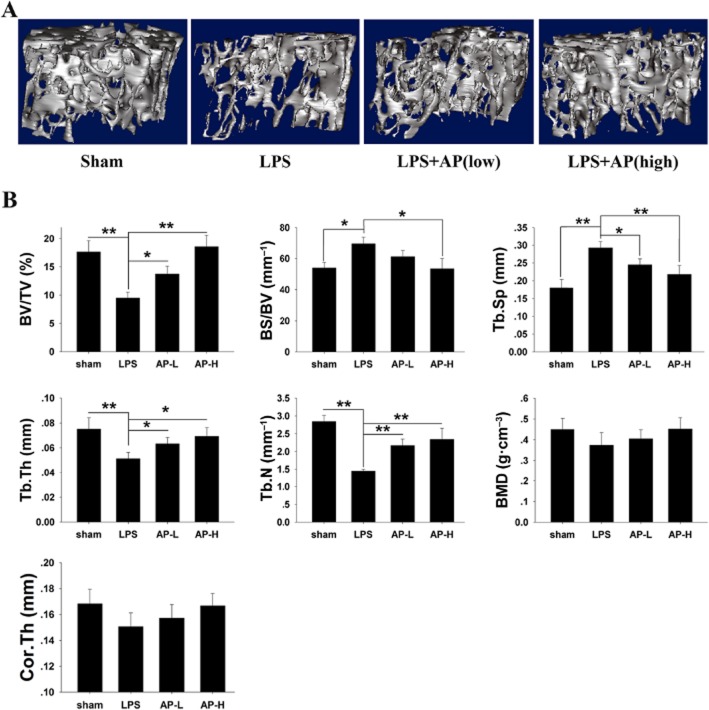
Figure 4.
AP prevented LPS-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity. Mice were injected intraperitoneally with AP (5 or 30 mg·kg−1 body weight) or PBS as a control 1 day before injection with LPS (5 μg·g−1 body weight). AP or PBS was injected intraperitoneally every other day for 8 days. LPS was injected intraperitoneally on days one and four. All mice were killed 8 days after the initial LPS injection. (A) The left femurs of all animals were scanned with a high-resolution micro-CT. (B) The calculation of the microstructural indices was performed with the micro-CT data as described in the Methods section, including bone volume per tissue volume (BV/TV), bone surface/volume ratio (BS/BV), bone mineral density (BMD), average cortical thickness for both cortices (Cor.Th), trabecular separation (Tb.Sp.), trabecular thickness (Tb.Th.), and trabecular number (Tb.N). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, significant differences as indicated; one-way ANOVA, with Student-Newman-Keul's test.