Figure 2.
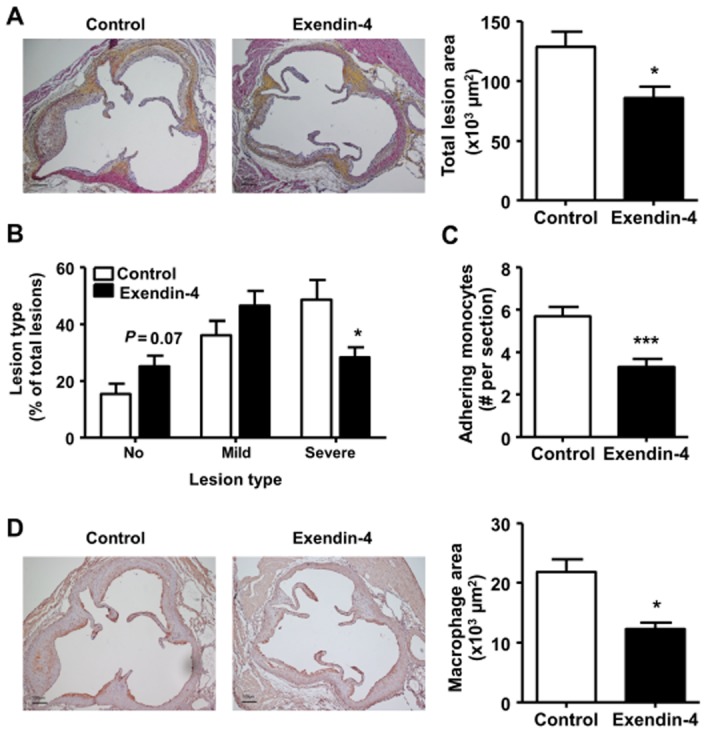
Exendin-4 reduces aortic atherosclerosis development and monocyte recruitment to the endothelium wall. After 5 weeks of feeding a Western-type diet containing 0.4% cholesterol, mice were treated with exendin-4 (50 μg·kg−1·day−1) or vehicle (PBS) s.c. for 4 weeks. Subsequently, hearts were isolated, fixed, dehydrated and embedded in paraffin. Cross sections of the aortic root were stained with haematoxylin-phloxine-saffron (A, B) or anti-AIA serum (C, D). Total lesion area (A), lesion severity (B), the number of adhering monocytes to the endothelium wall (C) and macrophage area (D) were quantified. Values are means ± SEM (n = 17 mice per group). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 compared with vehicle.
