Figure 8.
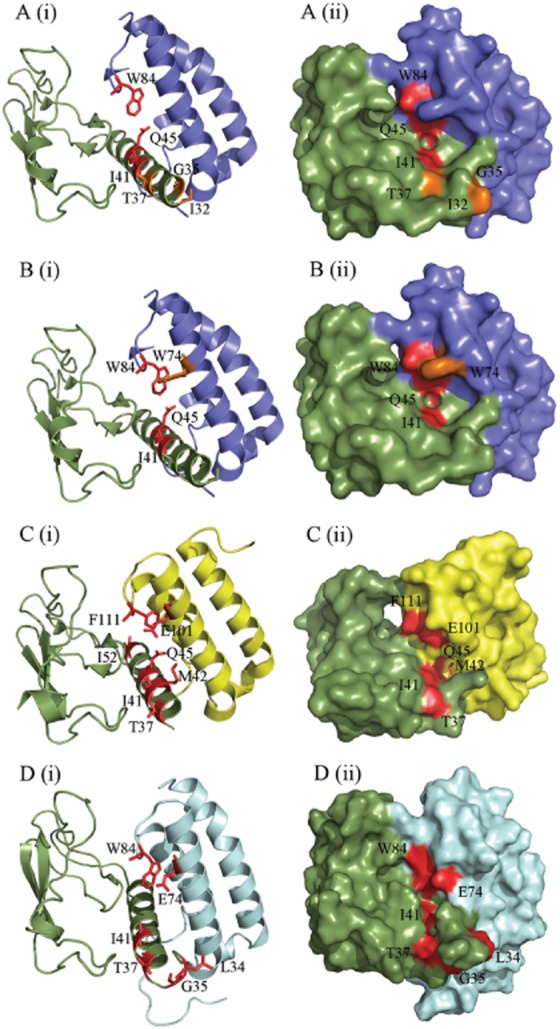
Figure depicting the amino acid residues likely to be involved in peptide binding, generated using PyMol. (A) CGRP-binding residues in the CGRP receptor ECD (3N7S; a representative structure for the CGRP receptor), as previously determined by alanine scanning mutagenesis (Barwell et al., 2010). (B) AM-binding residues in the CGRP receptor. (C) AM-binding residues in the AM1 receptor ECD (3AQF). The AM1 receptor structure is N-terminally truncated to V36; thus, many residues involved in AM binding could not be depicted. This may indicate increased mobility of this region of the receptor ECD. (D) AM-binding residues in our AM2 receptor ECD model. RAMP1 is shown in blue, RAMP2 in yellow, RAMP3 in pale blue and CLR in green. Residues where substitution resulted in a decrease in peptide potency are shown in red; those that cause an increase in potency are shown in orange. In each part of the figure, (i) shows secondary structural elements with residues involved represented as sticks and (ii) shows the surface map.
