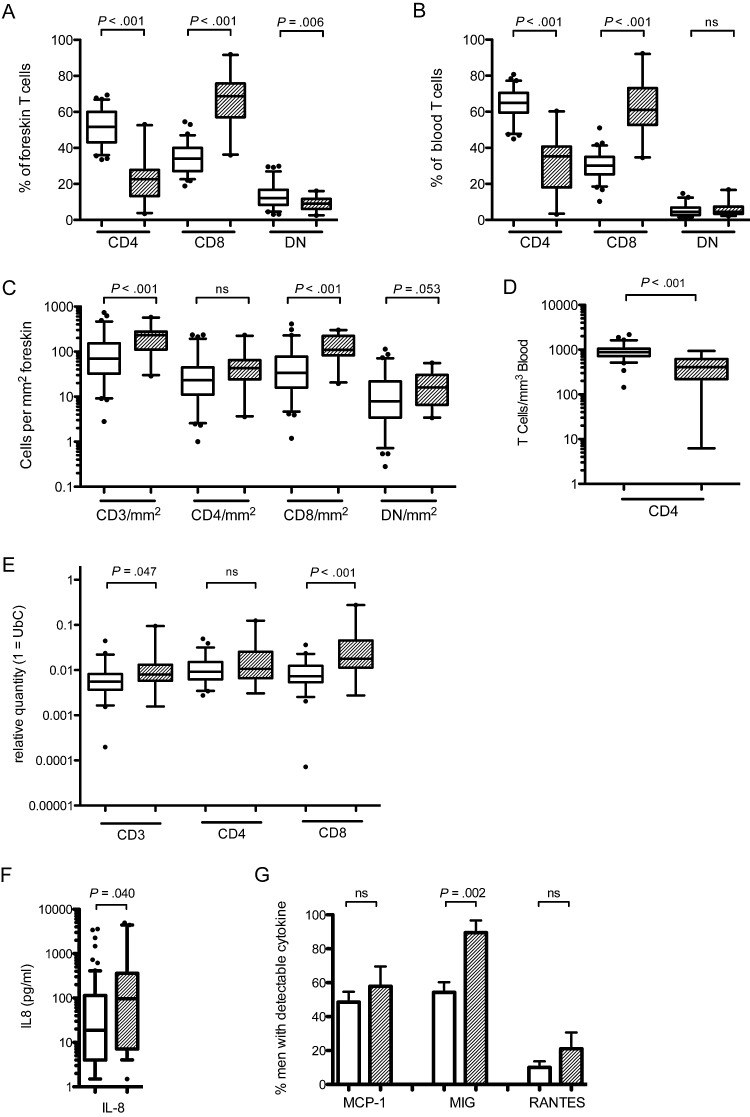
Figure 1.
T-cell subsets in the blood and foreskin of HIV-infected ( ) and uninfected (
) and uninfected ( ) men. Relative proportions of CD4, CD8, and double-negative (DN) CD3+ T cells were measured in the foreskin (A) and blood (B) using flow cytometry. Number of CD3 T cells per mm2 (C) was obtained through immunohistochemistry and used to calculate the absolute number of foreskin CD4, CD8, and DN T cells from flow cytometry proportions. The absolute numbers of blood CD4 T cells was obtained from clinical CD4 counts (D). Foreskin tissue quantities of T-cell markers were confirmed with PCR (E). Chemokine levels in the subpreputial space were assayed using a multiplex immunoassay system: IL-8 (F) was quantifiable in all swabs and was treated as a continuous outcome; detection of MIG, MCP-1, and RANTES was variable, and therefore presence of the chemokine was compared between HIV-infected and uninfected men (G). Statistical comparisons made by Mann–Whitney U test; CD3, CD4, and CD8 T-cell densities controlled for HSV-2 status by multivariate general linear regression and adjusted P values are reported.
) men. Relative proportions of CD4, CD8, and double-negative (DN) CD3+ T cells were measured in the foreskin (A) and blood (B) using flow cytometry. Number of CD3 T cells per mm2 (C) was obtained through immunohistochemistry and used to calculate the absolute number of foreskin CD4, CD8, and DN T cells from flow cytometry proportions. The absolute numbers of blood CD4 T cells was obtained from clinical CD4 counts (D). Foreskin tissue quantities of T-cell markers were confirmed with PCR (E). Chemokine levels in the subpreputial space were assayed using a multiplex immunoassay system: IL-8 (F) was quantifiable in all swabs and was treated as a continuous outcome; detection of MIG, MCP-1, and RANTES was variable, and therefore presence of the chemokine was compared between HIV-infected and uninfected men (G). Statistical comparisons made by Mann–Whitney U test; CD3, CD4, and CD8 T-cell densities controlled for HSV-2 status by multivariate general linear regression and adjusted P values are reported.
Abbreviations: HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HSV-2, herpes simplex virus 2; IL-8, interleukin 8; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; MIG, monokine induced by γ-interferon, PCR, polymerase chain reaction; RANTES, regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted.