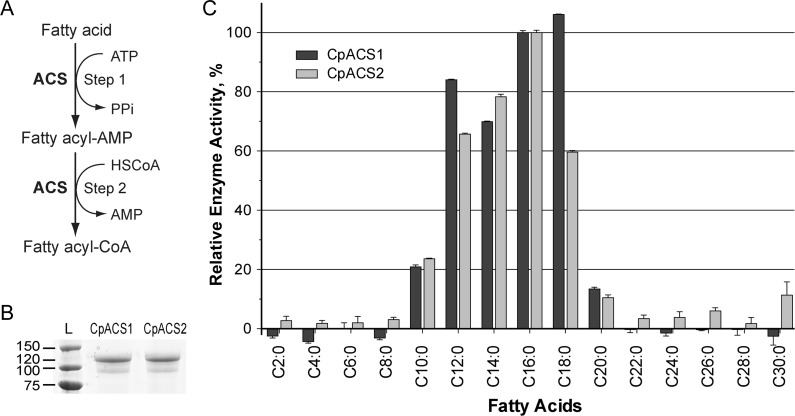
Figure 1.
Activation of long chain fatty acids by Cryptosporidium parvum acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) synthetase (ACS). A, Illustration of ACS-catalyzed 2-step reaction to form fatty acyl CoA from free fatty acid, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and CoA in reduced form (HSCoA). B, Purified recombinant CpACS1 and CpACS2 proteins fractionated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. C, Substrate preferences of recombinant CpACS1 and CpACS2 proteins toward variable carbon chain–length saturated fatty acids as determined by 5,5′-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoate) (DTNB) assay. Activities are expressed relative to C16 palmitic acid L, protein ladder (kDa).