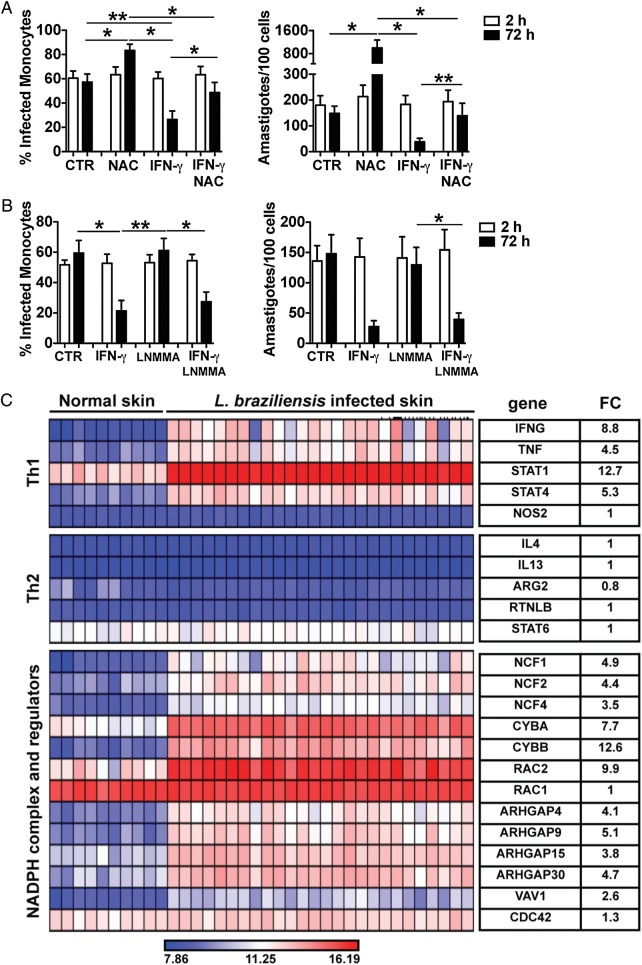
Figure 5.
ROS, but not NO, production is implicated in the control of Leishmania braziliensis in vitro and in the skin of L. braziliensis patients. Human monocytes were infected with amastigotes of L. braziliensis (2:1) and cytospins of cultures were performed at 2 and 72 hours. Cultures were assessed for the percentage of infected cells and the number of amastigotes per 100 cells using light microscopy. Cells were treated with or without (A) NAC, IFN-γ or NAC + IFN-γ; (B) LNMMA, IFN-γ or LNMMA + IFN-γ. Data from 6 donors from experiments performed independently are shown. *P ≤ .05; **P ≤ .01. (C) Heatmap showing induction of genes obtained from a microarray profiling of 26 human lesions and 10 normal skin biopsies. Average fold change (FC) for each gene in lesion samples, relative to normal skin controls, is shown. Abbreviations: IFN-γ, interferon γ; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; NO, nitric oxide; ROS, reactive oxygen species.