Figure 1.
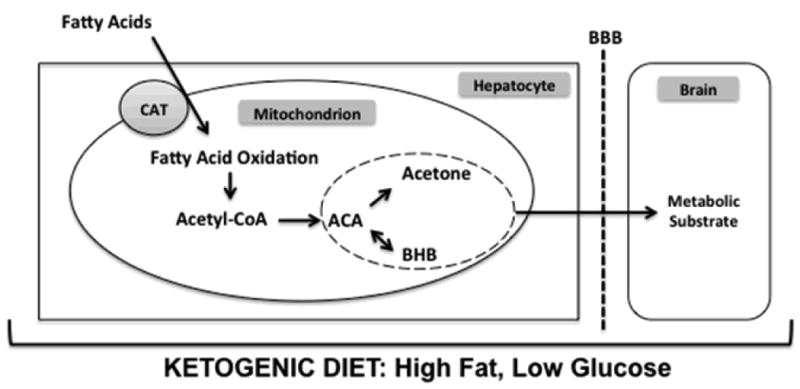
A high-fat, low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet causes a shift in the metabolic activity of hepatocytes. Under these conditions, the Krebs cycle can not utilize the high levels of acetyl-CoA generated from fat. Remaining acetyl-CoA is converted to the ketone body acetoacetate. The two additional ketone bodies, acetone and β-hydroxybutyrate, are derived from acetoacetate by spontaneous degradation and enzymatic conversion with β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, respectively. The three ketone bodies are then released from the hepatocyte, cross the blood brain barrier, and may exert their effects in the brain. Abbreviations: CAT, carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase; ACA, acetoacetate; BHB, β-hydroxybutyrate; BBB, blood brain barrier.
