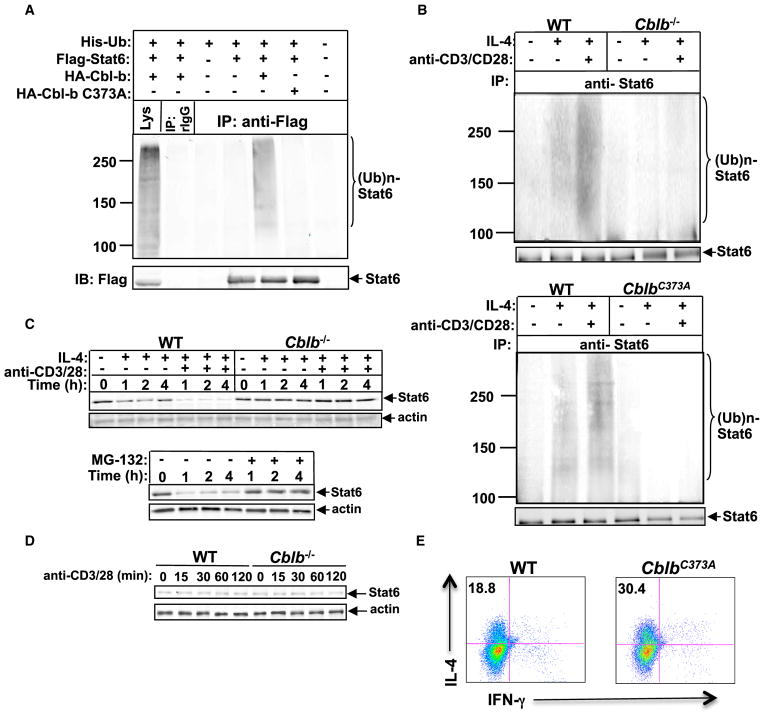
Figure 5. Cbl-b Is the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase for Stat6.
(A) IP of proteins from lysates of 293T cells transiently transfected with plasmids encoding with Flag-tagged Stat6, HA-tagged Cbl-b, or Cbl-b C373A mutant, and His-tagged ubiquitin with anti-Flag, followed by immunoblot analysis (IB) with anti-Flag and anti-HA, respectively.
(B) IP of proteins from CD4+ T cells from WT and Cblb−/− mice (top) or WT and CblbC373A mice (bottom) pretreated with MG-132 for 30 min, and stimulated with IL-4 in the presence or absence of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 with anti-Stat6, followed by immunoblotting with anti-ubiquitin and reblotting with anti-Stat6.
(C) Top: immunoblot analysis of total protein levels of Stat6 of WT and Cblb−/− CD4+ T cells stimulated for 1, 2, and 4 hr with IL-4 in the presence or absence of anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28. Bottom: immunoblot analysis of Stat6 protein expression of WT CD4+ T cells treated with anti-CD3, anti-CD28, and IL-4 for 1, 2, and 4 hr with or without MG-132. Actin was used as a loading control.
(D) Immunoblot analysis of Stat6 protein expression of WT and Cblb−/− CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 15, 30, 60, and 120 min.
(E) Intracellular staining of Th2 cells differentiated in vitro from purified naive CD4+CD25−CD62LhiCD44lo T cells of WT or CblbC373A mice. Numbers in the quadrants indicate the percentage of IL-4/IFN-γ-producing cells in the CD4+ population. Results are representative of three independent experiments.