Figure 2. Anatomy and transport in the blood-brain barrier.
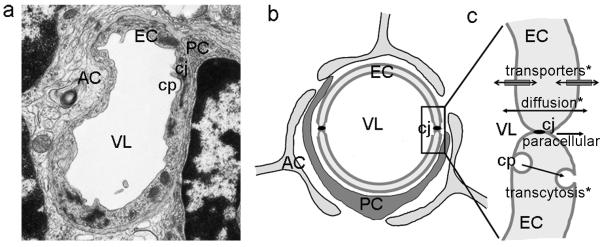
(a) Transmission electron microscopy of a capillary in the brain and its (b) schematic representation. Endothelial cells (EC) surrounding the vessel lumen (VL), with pericytes (PC) and feet of astrocytes (AC) adjacent to the endothelial layer. Endothelial cells display electron dense cell junctions (cj) sealing the cell-cell borders. A forming clathrin-coated pit (cp) can be observed in the endothelial luminal surface. (c) Transport of small and lipophilic molecules across the endothelial lining can occur between the cell junctions (the paracellular pathway, almost defunct in the BBB) or by diffusion across the cell. In addition, other pathways of transport across the cell layer include transporters located in the endothelia luminal and abluminal surfaces, as well as vesicular transcytosis (mainly mediated by clathrin-mediated mechanisms). * transcellular.
