Fig. 4.
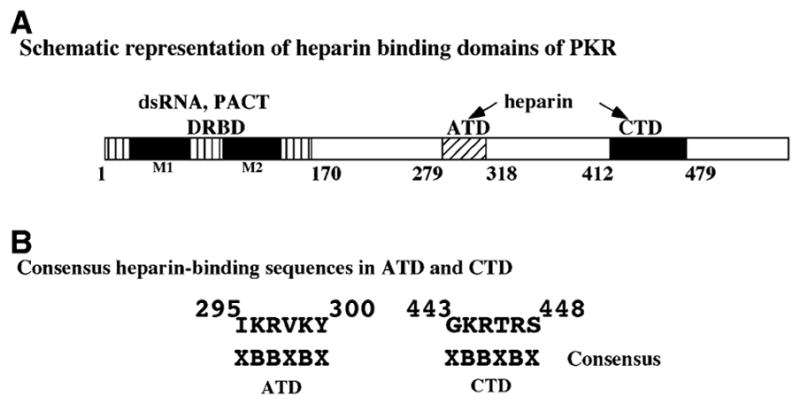
(A) Schematic representation of the heparin-binding domains of PKR. The relative positions of the domains involved in PKR binding to different activators are indicated. The dsRNA and PACT interacting domain is shown as a box with vertical lines and the two conserved motifs are shown as black boxes. The amino terminal heparin-binding domain (ATD heparin) is shown as a box with oblique hatch and the carboxy terminal heparin-binding domain (CTD heparin) is shown as a black box. (B) The two heparin-binding domains of PKR contain a consensus heparin-binding sequence XBBXBX. B indicates a basic residue and X indicates any residue. Residues 295–300 within ATD and residues 443–448 within CTD fit the consensus.
