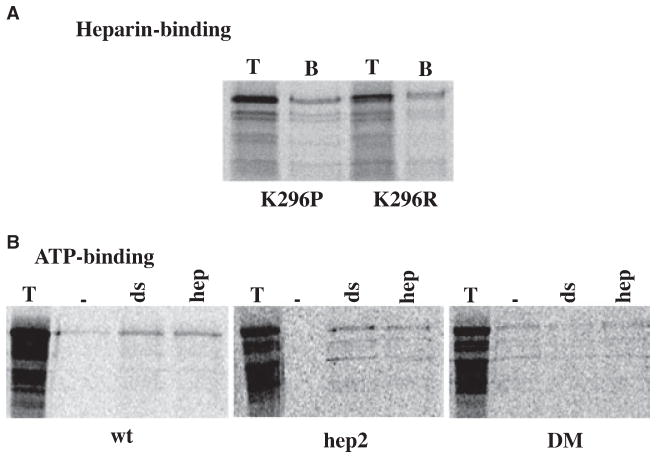
Fig. 7.
(A) K296 does not contribute to PKR’s heparin-binding activity. The heparin–agarose binding activity of K296R and K296P mutants was tested at 200 mM salt. T lanes represent 2 μL of the total proteins in the translation mix. The B lanes represent bound proteins at 200 mM salt. The top band indicates the positions of point mutants and the additional bands below the full-length protein band arise from initiations of translation at the internal methionines. (B) ATP-binding activity of hep2 and DM mutants. ATP-agarose binding was assayed for the mutants. 4 μL of the in vitro translated proteins were bound to ATP-agarose in binding buffer either in the absence of any activator or in the presence of 0.1 mg·mL−1 poly(I)·poly(C) or 50 mg·mL−1 of heparin. T lanes, total proteins present in the translation mixture; –lanes, proteins bound to the beads in the absence of activator; ds lanes, proteins bound to the beads in the presence of dsRNA and hep lanes, proteins bound to the beads in the presence of heparin. The names of the proteins are indicated below the panels and the additional bands observed below the expected bands in T lanes arise due to initiation of translation at internal AUG codons in rabbit reticulocyte system.