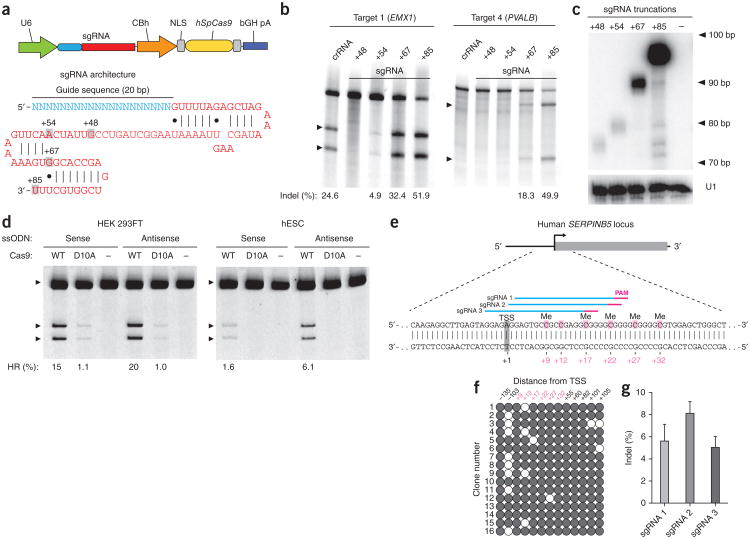
Figure 1.
Optimization of guide RNA architecture for SpCas9-mediated mammalian genome editing. (a) Schematic of bicistronic expression vector (PX330) for U6 promoter-driven sgRNA and CBh promoter-driven human codon-optimized S. pyogenes Cas9 (hSpCas9) used for all subsequent experiments. The sgRNA consists of a 20-nt guide sequence (blue) and scaffold (red), truncated at various positions as indicated. (b) SURVEYOR assay for SpCas9-mediated indels at the human EMX1 and PVALB loci. Arrowheads indicate the expected SURVEYOR fragments (n = 3). (c) Northern blot analysis for the four sgRNA truncation architectures, with U1 as loading control. (d) Both wild-type (WT) or nickase mutant (D10A) of SpCas9 promoted insertion of a HindIII site into the human EMX1 gene. Single-stranded oligonucleotides, oriented in either the sense or antisense direction relative to genome sequence, were used as homologous recombination templates (Supplementary Fig. 3). (e) Schematic of the human SERPINB5 locus. sgRNAs and PAMs are indicated by colored bars above sequence; methylcytosine (Me) are highlighted (pink) and numbered relative to the transcriptional start site (TSS, +1). (f) Methylation status of SERPINB5 assayed by bisulfite sequencing of 16 clones. Filled circles, methylated CpG; open circles, unmethylated CpG. (g) Modification efficiency by three sgRNAs targeting the methylated region of SERPINB5, assayed by deep sequencing (n = 2). Error bars indicate Wilson intervals (Online Methods).