Fig. 5.
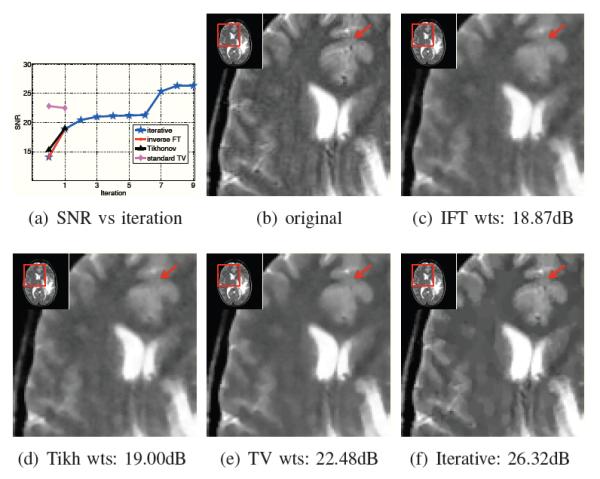
Comparison of current algorithms with pre-computed weights and the proposed iterative framework: We consider the reconstruction of the MRI brain image from 20% of its random Fourier samples using the H1 distance metric. In Fig. 5(a), we plot the improvement in signal to noise ratio as a function of the number of iterations. The zeroth iteration correspond to the different initial guesses. These guesses are derived with three different algorithms: zero filled inverse FFT (red), Tikhonov reconstruction (black), and local TV (majenta). Since the current NL schemes do not re-estimate the weights, only one iteration is involved. The blue curve corresponds to the proposed iterative scheme, which re-estimates the weights from the current image estimate. Since this scheme is also initialized with the zero filled IFFT, the red and the blue curves overlap. Note that the proposed iterative method provides significantly improved reconstructions.
