Fig. 6.
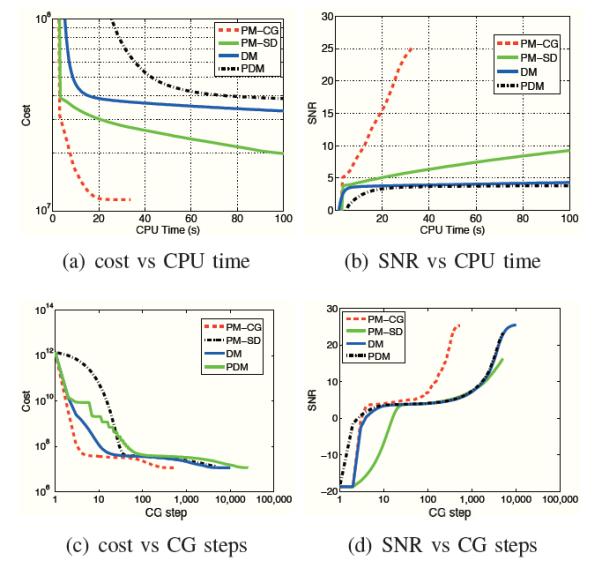
Comparison of optimization algorithms: We focus on the recovery of a 128 × 128 Shepp-Logan phantom from 16 radial lines in the Fourier domain by minimizing (12). The decay of the cost function (12) as a function of the number of conjugate gradient steps (inner iterations) and CPU time are shown in (a) and (b), respectively. The improvement in SNR as a function of iterations and CPU time are shown in (c) and (d), respectively. Note that all the optimization algorithms converge to the same minima. However, the PMCG scheme requires much fewer (20 fold) number of iterations. Moreover, the computational complexity per iteration of this method is also lower since the expensive weight computation is only performed in the outer loop.
