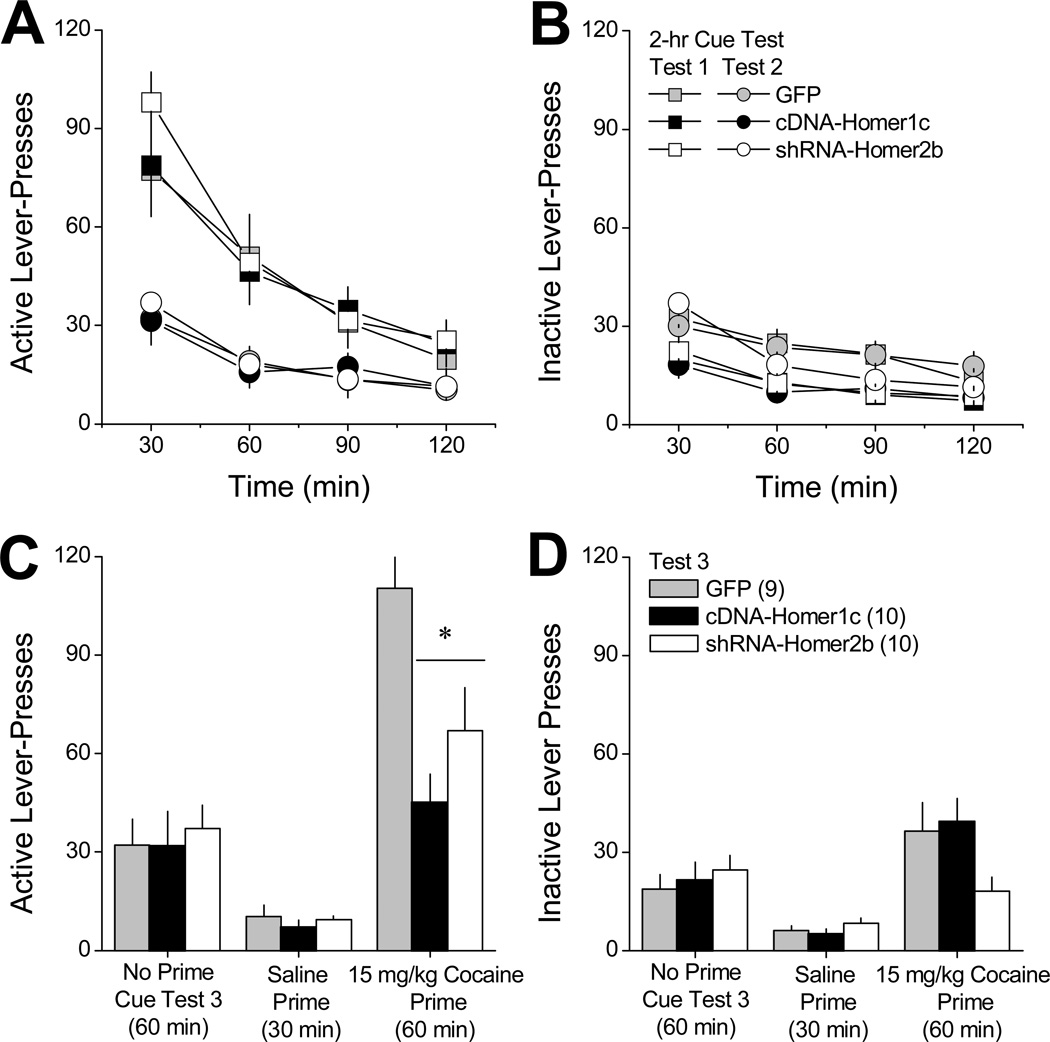
Figure 2. Reversing the cocaine-induced imbalance in vmPFC Homer1 versus Homer2 isoforms attenuates cocaine-primed reinstatement of drug-seeking.
Summary of the lever-pressing behavior emitted by rats with a 10-day history of intravenous cocaine (6h/day) that were infused intra-vPFC with AAVs carrying a GFP control vector (GFP), cDNA to over-express Homer1c (cDNA-Homer1c) or a shRNA to knock-down Homer2b (shRNA-Homer2b) prior to a 30-day withdrawal period. A and B, Time-course of active and inactive lever-pressing (in 30-min blocks) exhibited by the 3 AAV groups during an initial test for cue-reinforced responding, conducted at 30 days withdrawal (Test 1; squares) and during a subsequent cue test session, conducted the next day (Test 2; circles). C and D, Mean number of active and inactive lever-presses exhibited by the 3 AAV groups during a final test for cue-reinforced responding, in which rats were first allowed to lever-press under extinction conditions for 60 min in the absence of any manipulation (Extinction). Rats were then injected intraperitoneally with saline and allowed to respond for an additional 30 min (Saline), followed by a 15 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of cocaine and an additional 60 min of testing (Cocaine). All data represent the mean ± SEM of the number of animals indicated in parentheses in panel B. *p<0.05 vs. GFP (LSD post-hoc tests).