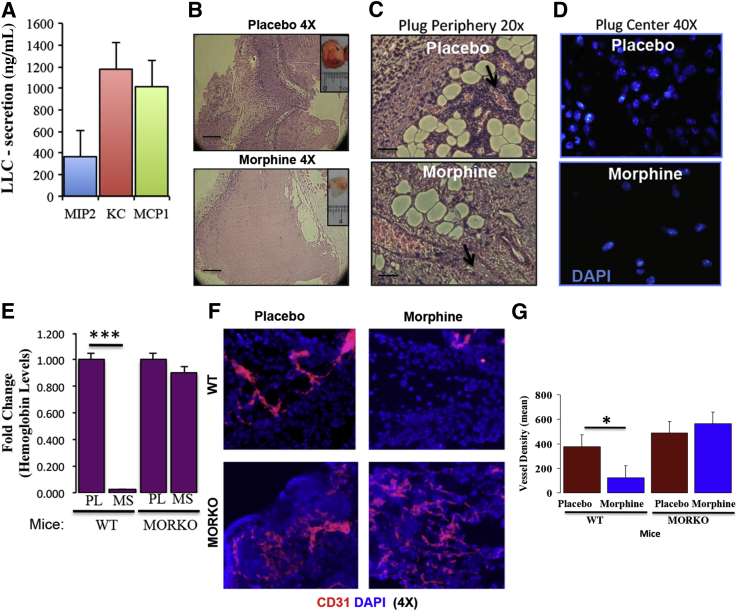
Figure 2.
A: Effect of morphine on leukocyte infiltration. LLC cells secrete chemotactic factors as determined using an ELISA. LLC-CM–induced leukocyte infiltration as seen in H&E-stained Matrigel plugs (inset) taken from placebo- and morphine-treated mice (B) (n = 5 per group); leukocyte accumulation near blood vessels (arrows) at the plug periphery (C) and cell nuclei using DAPI stain on sections showing plug centers (D). E: Graph shows relative hemoglobin levels of Matrigel plugs removed on day 7 and determined using a standard curve from WT and MORKO mice (n = 4 per group) implanted with either placebo or morphine. F: Fluorescent captured images of CD31-PE–stained (red) Matrigel plug (containing 100 ng/mL of VEGF) sections taken from WT and MORKO placebo and morphine pellet implanted mice. G: Quantification of blood vessel density using morphometric analysis. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗∗P < 0.005. Scale bars: 100 μm (B); 20 μm (C and D). Original magnification ×4 (B); ×20 (C and D).