Fig. 4.
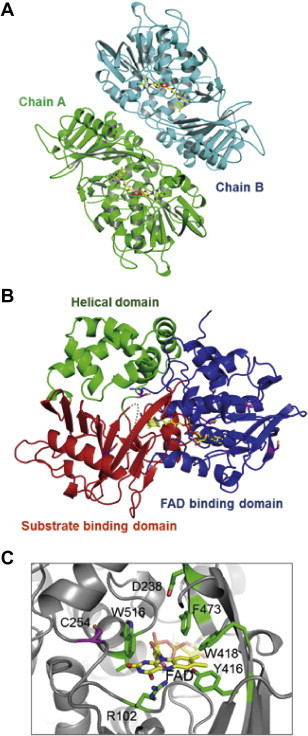
Crystal structure of l-AAO/MOG. (A) Dimer structure contained in the asymmetric unit. A and B chains are colored green and cyan, respectively. FAD molecules are shown as yellow sticks. (B) Monomer structure. FAD binding domain, substrate binding domain, and helical domain are colored blue, red, and green, respectively. Six Cys residues are shown as magenta. A disordered region (residues 419–428) is indicated by a grey dash line. (C) The active site. An “aromatic cage” is formed by Phe-418, Phe-473, Trp-516, and re-face of the isoalloxazine ring of FAD. Cys-254, the critical residue for conversion of l-AAO/MOG activities, is positioned behind Trp-516. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
