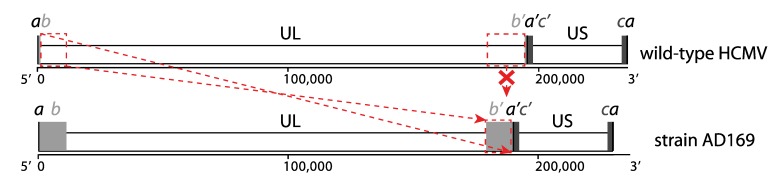
Figure 1.
Class E genome of HCMV. The unique long and unique short regions are indicated as UL and US. Repeat regions are indicated as a, b and c sequences, where primes designate inverted orientations. Sequences ab and b’a’ correspond to the terminal/internal repeat long (TRL/IRL); sequences a’c’ and ca correspond to the internal/terminal repeat short (IRS/TRS). Top: typical genome arrangement of wild-type strains; bottom: genome arrangement of strain AD169 is given as an example of a laboratory-adapted strain. Genome rearrangements (deletion of UL 3’ end and replacement by an inverted copy of UL 5’ end) that have occurred during extensive passaging are indicated in red between the wild-type and laboratory-adapted configurations.