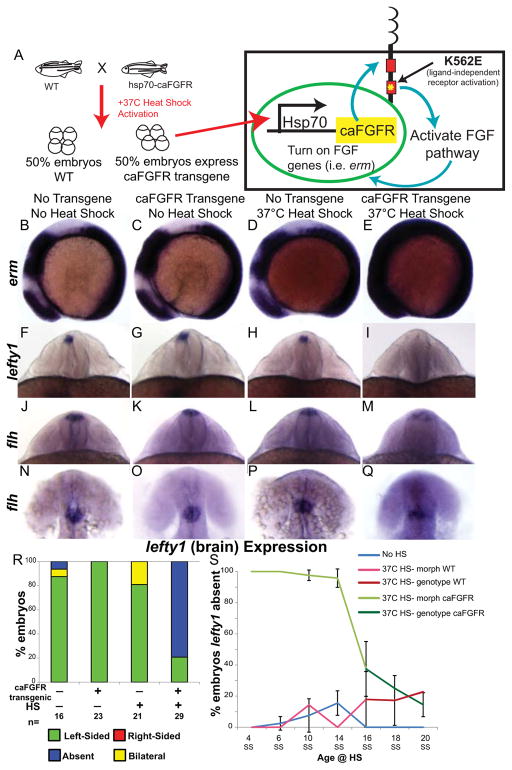
Figure 2. FGF pathway controls brain asymmetry.
(A) Diagram of heat-shock (HS) activation of the FGF pathway by expression of a constitutively active FGFR1 (caFGFR) protein with a K562E point mutation to activate downstream targets of FGF signaling. (B–E) Lateral view of erm expression in 8 somite embryos. Normal expression of erm in a non-HS’d non-transgenic embryo (B; WT expression 100%, n=24). No up-regulation of erm expression in either a caFGFR transgenic non-HS’d embryo (C; WT expression 100%, n=19) or a non-transgenic HS’d embryo (D; WT expression 93.3%, n=15). However, a dramatic increase in erm expression in a HS’d transgenic embryo (E; Increased expression 73.17%, n=41). (F–I) Dorsoposterior view of 22–24 somite embryos expressing lefty1 (brain). Normal left-sided expression of lefty1 in non-transgenic non-HS’d (F), transgenic non-HS’d (G), and non-transgenic HS’d (H) control embryos. Contrary to normal expression in control embryos lefty1 expression is absent in the brain of transgenic HS’d embryos (I). (J–M) Dorsoposterior and (N–Q) dorsal views of distinct 22–24 somite embryos expressing flh. Normal expression of flh in the dorsal diencephalons of non-transgenic non-HS’d (J, N; n=19 WT expression), transgenic non-HS’d (K, O; n=10 WT expression), and non-transgenic HS’d control embryos (L, P; n= 17 WT expression). Expression of flh is detected in the dorsal brain of caFGFR transgenic HS’d embryos (M, Q; n=23 present but dispersed expression), but appears to be more dispersed. (R) Histogram quantifying the expression of lefty1 in the brain of genotyped embryos. (S) Line graph illustrating the timeline over which FGF signaling controls lefty1 expression in the brain. Embryos that were HS’d caFGFR before 14SS can be clearly identified by changes in morphology, as confirmed by genotyping (panel 2R). Therefore, embryos HS from 4 SS to 14 SS were classed as follows: HS Morph WT (HS non-transgenic siblings), HS Morph caFGFR (HS transgenic siblings). Embryos HS from 16 SS to 20 SS cannot be distinguished by morphological phenotype, so they were individually genotyped, and were classed as follows: HS non-transgenic siblings (HS genotype WT), HS transgenic siblings (HS genotype caFGFR). 4 SS: No HS n=50, 37C HS- morph WT n=27, 37C HS- morph caFGFR n=30; 6 SS: No HS n=91, 37C HS- morph WT n=42, 37C HS- morph caFGFR n=35; 10 SS: No HS n=40, 37C HS- morph WT n=28, 37C HS- morph caFGFR n=29; 14 SS: No HS n=39, 37C HS- morph WT n=34, 37C HS- morph caFGFR n=26; 16 SS: No HS n=51, 37C HS- genotype WT n=27, 37C HS- genotype caFGFR n=30; 18 SS: No HS n=33, 37C HS- genotype WT n=24, 37C HS- genotype caFGFR n=28; 20 SS: No HS n=42, 37C HS- genotype WT n=23, 37C HS- genotype caFGFR n=16.