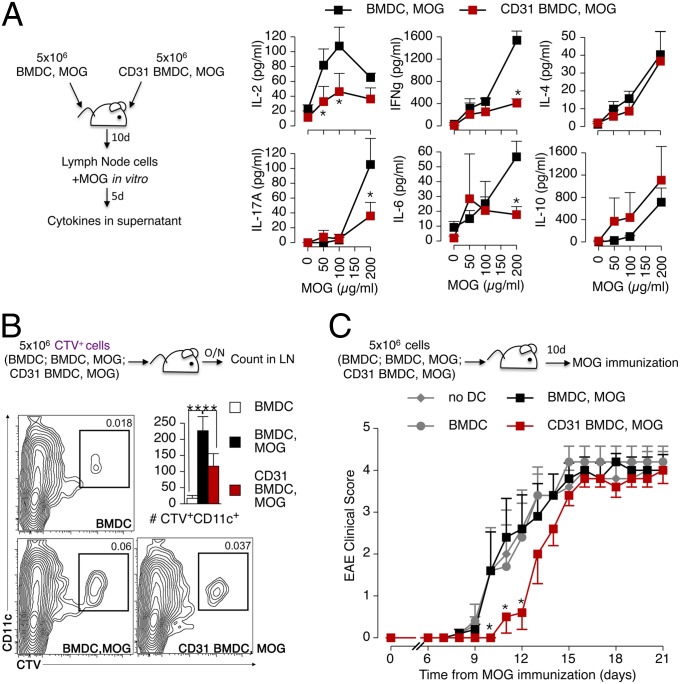
Fig. 7.
CD31-conditioned BMDCs confer tolerance against autoimmune responses in vivo. (A) BMDCs and CD31-conditioned BMDCs (CD31 BMDCs) were stimulated with LPS overnight as described above, and MOG peptide 35–55 was added during the last 4 h. The cells were injected s.c. (total of 5 × 106 cells per mouse) in C57BL/6 mice. The draining lymph node cells of the recipient mice were harvested 10 d later and stimulated with increasing concentrations of the MOG peptide for 5 d in vitro. Cytokine release, analyzed by CBA in the supernatant, showed that CD31-conditioned BMDCs were not able to induce the production of IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-17A, and IL-6 by MOG-specific CD4+ T cells. Intriguingly, the production of IL-4 and IL-10 was similarly abundant in the two conditions. *P < 0.05. (B) Flow cytometry tracking of adoptively transferred CTV+ BMDCs, identified as CD11c+, showed that fewer CD31 BMDC, MOG cells reached the draining lymph nodes compared with BMDC, MOG cells. **P < 0.01. (C) Potential tolerogenic properties of CD31 BMDC, MOG cells were evaluated in vivo by active MOG immunization 10 d after the adoptive transfer. The transfer of CD31 BMDC, MOG cells delayed the development of EAE. A minimum of three mice per group were used in each condition, and the experiments were repeated twice, with similar results. *P < 0.05.