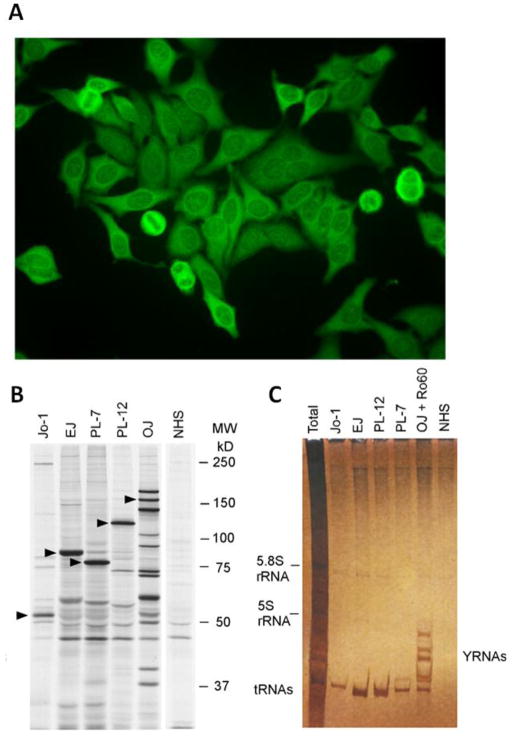
Figure 1.
Detection of anti-ARS autoantibodies. A.) The classical indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) pattern of an anti-Jo-1 autoantibody positive sample is characterized by diffuse cytoplasmic staining on HEp-2 cells. Autoantibodies to other synthetases can show similar staining patterns. To differentiate the pattern from other cytoplasmic patterns (i.e. anti-ribososmal P autoantibodies), the absence of nucleolar staining is an important discriminator. It should be noted that less than half of the sera that have identifiable anti-Jo-1 will demonstrate this typical IIF pattern. The specific proteins identifying each autoantibody are marked with triangles. B.) Characterization of various anti-ARS autoantibodies (anti-Jo-1, PL-7, PL-12, OJ, EJ) by protein immunoprecipitation using 35S-methionine-labeled K562 cell lysates, SDS-PAGE and autoradiography is shown (courtesy of Dr. Minoru Satoh). C.) Immunoprecipitation profile of cytoplasmic RNAs using phenol/chloroform extraction and urea-PAGE followed by silver staining demonstrating the typical tRNAs associated with each of the anti-ARS autoantibodies (courtesy of Dr. Minoru Satoh).