Fig. 14.
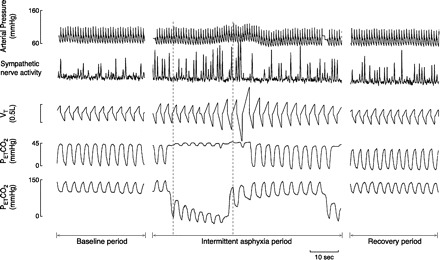
In healthy humans, brief (20-min) exposure to intermittent asphyxia causes sympathetic activation that persists after normalization of blood gases, not only during the interasphyxia phases, but also in the room air recovery period. [From Xie et al. (736).]
