Figure 1.
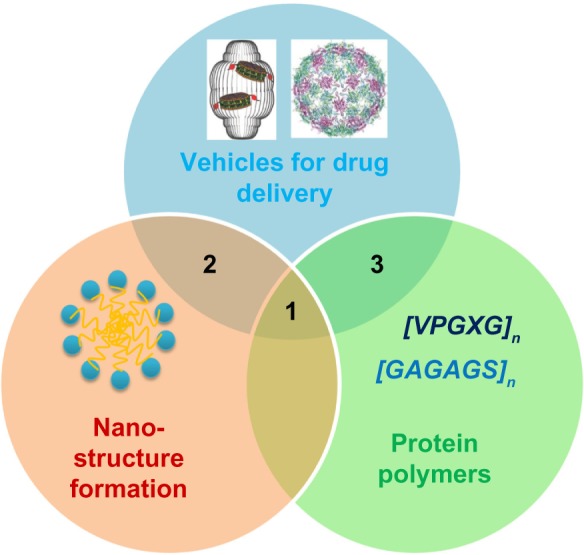
Design of genetically engineered drug carriers.
Notes: The field of biological nanomedicine (aka “BioNano”) is emerging at the intersections between genetically engineered biomaterials, nano-assembly, and protein polymers. At intersection 1, nanomedicines are being developed from protein polymers (eg, ELP, SLP, and SELP). At intersection 2, protein-based materials (eg, viral capsids and vault proteins) are being developed as platforms for assembly of nanostructures. At intersection 3, proteins that avoid structure formation (eg, intrinsically disordered proteins and XTEN fusion proteins) are being explored for their ability to alter biodistribution and efficacy.
Adapted with permission from Galaway FA, Stockley PG. MS2 viruslike particles: a robust, semisynthetic targeted drug delivery platform. Mol Pharm. 2013;10(1): 59–68.55 Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society, and Buehler DC, Toso DB, Kickhoefer VA, Zhou ZH, Rome LH. Vaults engi neered for hydrophobic drug delivery. Small. 2011;7(10):1432–1439.7 Copyright 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Abbreviations: ELP, elastin-like polypeptide; SLP, silk-like polypeptide; XTEN, extended recombinant polypeptide.
